42 Substances of abuse
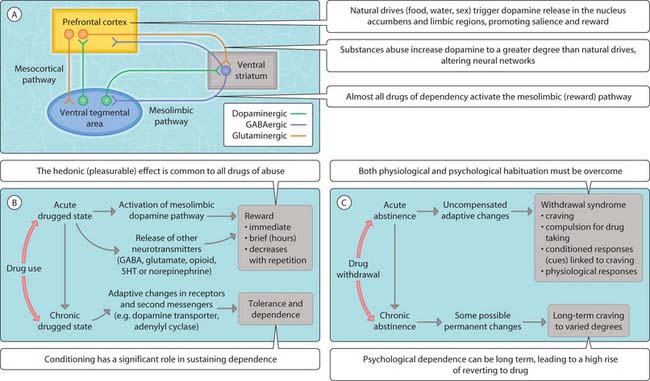
A number of substances repeatedly taken either legally (nicotine, alcohol) or illegally (amphetamine, cocaine, heroin) can give rise to substance dependence. Substances of abuse increase the mesocortical and mesolimbic dopaminergic pathways associated with salience and reward for natural drives (e.g. food, water and sex) that originate in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) and project to the prefrontal cortex and limbic system. Neuroadaptive changes promote craving, compulsion for drug taking, conditioned response (i.e. cues) linked to craving (e.g. desire to smoke in a social setting), tolerance and withdrawal symptoms (Fig. 3.42.1).
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue