183 Sturge–Weber syndrome (encephalotrigeminal angiomatosis)
Salient features
Examination
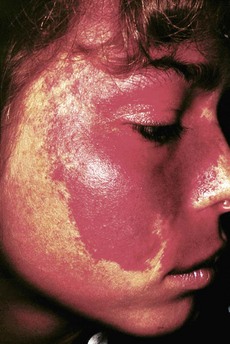
• A port-wine stain is present on the face in the distribution of the first and second division of the trigeminal nerve (Fig. 183.1)
• Look for haemangiomas of episclera and iris
• Tell the examiner that you would like to:
• examine the fundus for unilateral choroidal haemangiomata: the so-called haemangioma is in almost all cases on the side of the facial naevus flammeus and is so diffuse that the colour change it causes is commonly called a ‘tomato ketchup’ fundus (Fig. 183.2)
• do a skull radiograph or cranial CT (Fig. 183.3) for intracranial ‘tramline’ calcification, particularly in the parieto-occipital lobe (caused by mineral deposition in the cortex beneath the intracranial angioma)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree