Strongyloidiasis
Key Facts
Terminology
Synonyms
Cochin China diarrhea, thread worm infection
Definition
Parasitic infection caused by nematode
Clinical Issues
Epidemiology
Worldwide distribution
More common in tropical countries
High in conditions that promote fecal contamination
Symptoms
Urticaria
Cough
Dyspnea
Hemoptysis
Bronchopneumonia
Intermittent diarrhea
Laboratory tests
Eosinophilia
Leukocytosis
Feces study is important in diagnosis
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) for IgG antibodies to antigens of larvae of Strongyloides
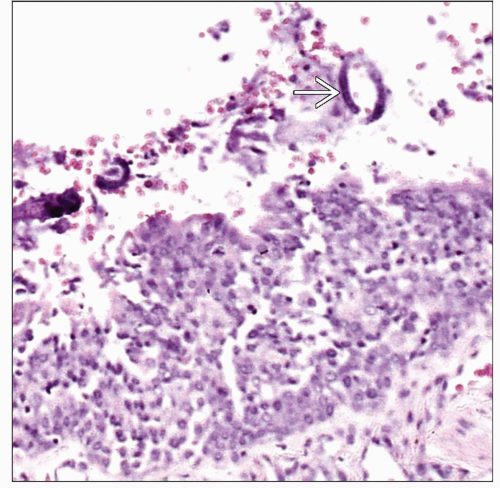
Microscopic Pathology
Inflammatory reaction with prominent eosinophils
Suppurative exudate
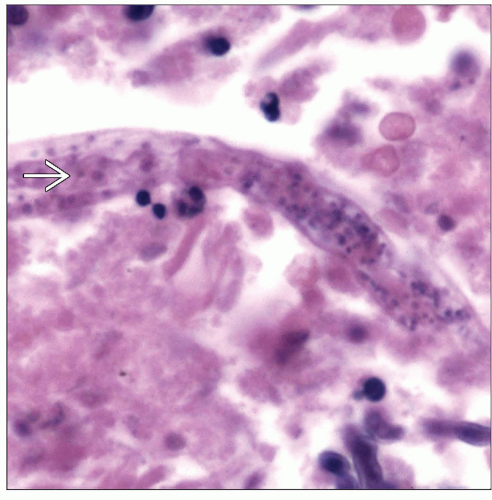
Presence of larvae
Presence of adult worm
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Cochin China diarrhea, thread worm infection
Definitions
Parasitic infection caused by a nematode
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Infectious Agents
Strongyloides stercoralis
3 Cycles of Infection
Direct
Filariform larvae penetrate the skin
Cutaneous phase may last a few days
Indirect
Rhabditiform larvae mature into free-living males and females in the soil
Autoinfection
Rhabditiform larvae become infective filariform larvae in intestine or skin of the host
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Worldwide distribution
More common in tropical countries
High in conditions that promote fecal contamination
Age
Affects any age group
Gender
Infection may be more common in males
Ethnicity
No ethnic predisposition
Presentation
Skin itching
Skin edema
Urticaria
Low-grade fever
Cough
Dyspnea
Hemoptysis
Bronchopneumonia
Intermittent diarrhea
Cramping
Constipation
Anemia
Asymptomatic
Laboratory Tests
Eosinophilia
Leukocytosis
Feces study is important in diagnosis
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) for IgG antibodies to antigens of larvae of Strongyloides
Treatment
Drugs
Thiabendazole
Albendazole