Squamous/Adenosquamous Carcinoma, Gallbladder
Joseph Misdraji, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Squamous cell carcinoma shows only squamous differentiation whereas adenosquamous carcinoma shows both glandular and squamous differentiation
Clinical Issues
1.4-9.6% of gallbladder carcinomas
Generally poor prognosis but depends upon grade, stage, and ability to achieve curative resection
Macroscopic Features
Most arise in gallbladder fundus as nodular masses or diffusely involve the gallbladder
Microscopic Pathology
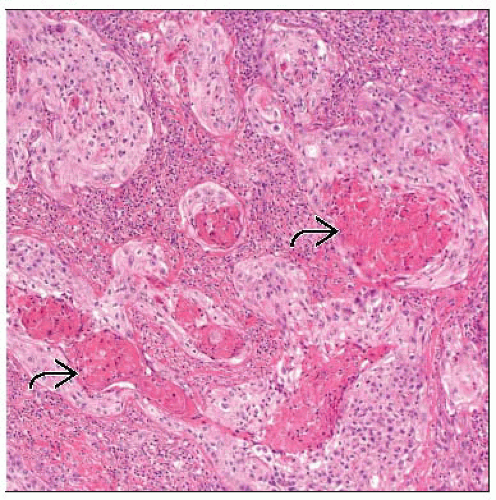
Glandular component can be intestinal, foveolar, papillary, or other pattern of cholangiocarcinoma
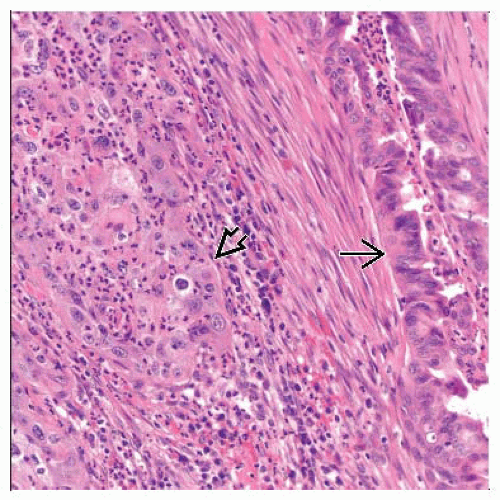
Squamous component shows whorls, keratin pearls, keratinization, &/or intercellular bridges
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Squamous cell carcinoma of gallbladder is rare variant of gallbladder cancer with only squamous differentiation
Adenosquamous carcinoma of gallbladder is uncommon variant of gallbladder cancer with both glandular and squamous differentiation
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Neoplastic
Several theories exist to explain origin of squamous component
Squamous metaplasia of gallbladder mucosa
Stepwise molecular progression from preexisting adenocarcinoma of gallbladder
Mapping of tumors has shown squamous components in deeper portions of tumor
Flow cytometric data have demonstrated DNA heterogeneity between glandular and squamous components in over 70% of cases
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree