Soft Tissue, Bone, and Joints
Atif Ahmed
▪ Questions and Answers
1. Joint stiffness and decreased mobility of the joints are features of all of the following conditions EXCEPT:
a. Gout
b. Arthrogryposis
c. Multiple pterygium syndrome
d. Homocystinuria
e. Osteoarthritis
View Answer
1. d. Joint stiffness can be congenital or acquired. Arthrogryposis refers to joint contractures observed at birth. Immobility interferes with limb development and causes joint fixation and formation of pterygia. Acquired inflammatory conditions such rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis lead to joint pain and stiffness. On the other hand, patients with Marfan syndrome or homocystinuria have increased mobility of the joints.
2. An aspirate of a lytic bone lesion in the rib yielded the large cells shown (Fig. 4.1). These cells are:
a. Myeloma cells
b. Langerhans histiocytes
c. Osteoblasts
d. Osteoclasts
e. Gaucher cells
d. Hypoparathyroidism
e. Pituitary adenoma
View Answer
2. c.These are osteoblasts with characteristic plasmacytoid cytoplasm. The nuclei, however, do not look like plasma cells. Osteoclasts can also be seen in bone aspirates but have multiple nuclei. Langerhans and Gaucher cells have characteristic morphology not observed in this smear.
3. Short stature can result from of all the following metabolic conditions EXCEPT:
a. Congenital hypothyroidism
b. Hereditary fructosemia
c. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
d. Malignant fibrous histiocytoma with cartilaginous differentiation
e. Pulmonary hamartoma
View Answer
3. b. Short stature with kyphosis and delay in ossification is a feature of congenital hypothyroidism. Pseudohypoparathyroidism is caused by defects in receptors and leads to obesity, short stature, and shortening of metacarpals, metatarsals, and phalanges. Hypoparathyroidism occurs in DiGeorge syndrome and also can be associated with short stature. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia, growth hormone deficiency, hypopituitarism resulting from adenomas can all lead to retardation of growth in children.
4. Rickets-like radiologic changes are characteristically seen in all of the following disorders EXCEPT:
a. Vitamin C deficiency, “scurvy”
b. Vitamin D deficiency
c. Chronic liver disease
d. Hypophosphatasia
e. Hypophosphatemia
View Answer
4. a. Rickets or osteomalacia results from conditions leading to impaired availability of vitamin D, decreased alkaline phosphatase, or increased loss of phosphates in urine. On the other hand, scurvy is characterized by inability to form extracellular collagen, which leads to osteopenia, demineralization, subperiosteal hemorrhage, and microfractures.
5. Fibrous dysplasia occurring in a patient with caféaulait skin spots is a characteristic of:
a. Xeroderma pigmentosa
b. Tuberous sclerosis
c. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome
d. Neurofibromatosis
e. McCune-Albright syndrome
View Answer
5. e. McCune-Albright syndrome compromises polyostotic fibrous dysplasia, skin pigmentation, and precocious puberty. Somatic mutations in the G signal transduction protein have been found in persons with this syndrome. The syndrome also causes variety of bony and endocrine abnormalities including hyperthyroidism.
6. Syndromes associated with “tall stature” include all of the following diseases EXCEPT:
a. Klinefelter syndrome
b. Homocystinuria
c. Marfan syndrome
d. Turner syndrome
View Answer
6. d. Tall stature can result from growth hormonesecreting tumors, thyrotoxicosis, homocystinuria, and Klinefelter and Marfan syndromes. Patients with Turner syndrome are typically short females with broad chest, wide spacing of the nipples, and congenital lymphedema of the neck, and have 45XO chromosomal pattern.
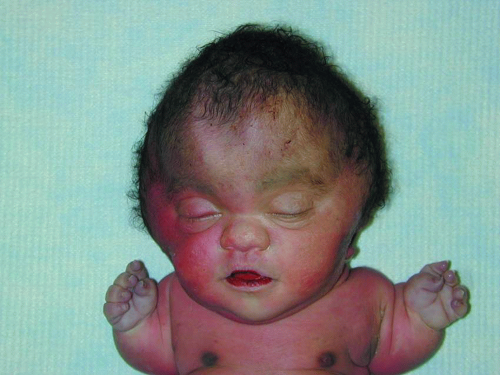
7. This baby (Fig. 4.2) was born at 35 weeks of gestation and died a few days after birth with respiratory failure. The diagnosis is:
a. Potter sequence
b. Down syndrome
c. Skeletal dysplasia
d. Thalassemia major
e. “Overgrowth” syndrome
View Answer
7. c. Combination of short extremities, narrow thorax, and frontal bossing with cloverleaf-like skull configuration is consistent with a skeletal dysplasia. Patients with skeletal dysplasia usually die of respiratory failure due to lung hypoplasia.
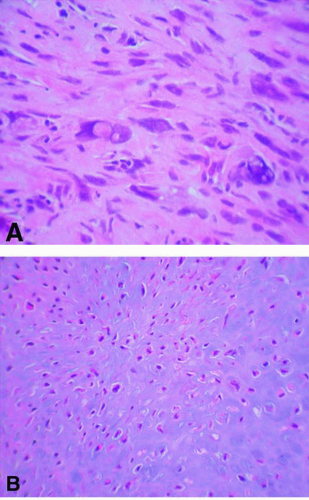
8. This CD99-positive tumor (Fig. 4.3) is found in the metaphyseal region of the right femur of a 15-year-old
boy. The differential diagnosis should include all of the following EXCEPT:
boy. The differential diagnosis should include all of the following EXCEPT:
a. Lymphoma
b. Ewing sarcoma
c. Osteosarcoma
d. Synovial sarcoma
e. Chondrosarcoma
View Answer
8. e. CD99 positivity is traditionally associated with Ewing sarcoma/PNET. However, some lymphomas, small cell osteosarcoma, and monophasic synovial osteosarcoma can all stain with CD99.
9. Which of the following statements best describes elastofibroma?
a. It is a well-circumscribed nodule occurring in the face of adults.
b. It is composed of alternating bands of collagen and elastic fibers.
c. It is found in the scapular region of young children.
d. It is related to injury associated with birth.
e. It is a rapidly growing tumor following trauma.
View Answer
9. b. Elastofibroma is a benign, poorly circumscribed reactive tumor condition occurring exclusively in the scapular region of elderly people and is characterized by large numbers of prominent elastic fibers.
10. These are sections of a metastatic tumor in the lung of a 16-year-old boy (Fig. 4.4). The diagnosis is most likely:
a. Pleomorphic sarcoma
b. Chondrosarcoma
d. Malignant fibrous histiocytoma with cartilaginous differentiation
e. Pulmonary hamartoma
View Answer
10. c. Osteosarcoma is the most likely diagnosis in this age group and can have cartilaginous differentiation. Thin osteoid can be seen in between the tumor cells in the left upper quadrant of the first image. Chondrosarcoma and malignant fibrous histiocytoma are rare in this age group.
11. Grading of soft tissue sarcomas depends on all of the following histologic features EXCEPT:
a. The degree of resemblance to normal adult mesenchymal tissue
b. The number of mitotic figures per 10 fields
c. The degree of tumor necrosis
d. Expression of P53
e. The histologic type of the tumor
View Answer
11. d. Grading of sarcomas emphasizes tumor differentiation, number of mitotic figures, and tumor necrosis. For example, tumors with >5 mitosis/10 HPF and >15% necrosis are considered high grade or grade III. Certain tumors are by definition high grade, such as alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma.
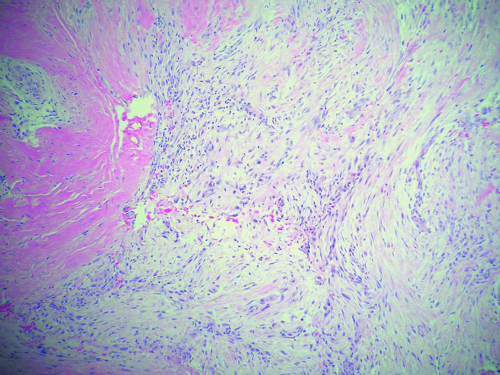
12. A 25-year-old man developed a painless lump in his right arm (Fig. 4.5) that started to grow 3 weeks after playing in a football match. Which of the following statements apply to this lesion?
a. It needs to be reexcised with adequate margin because of its malignant potential.
c. The tumor cells characteristically stain with CD34 and S-100.
d. It rarely recurs after excision.
e. It occurs chiefly in older individuals and the elderly.
View Answer
12. d. Nodular fasciitis grows rapidly after trauma and usually affects children and young adults between 20 to 40 years of age. The tumor can have spontaneous regression and does not usually recur after excision. It can involve the skull bones but is considered a reactive nonneoplastic process.
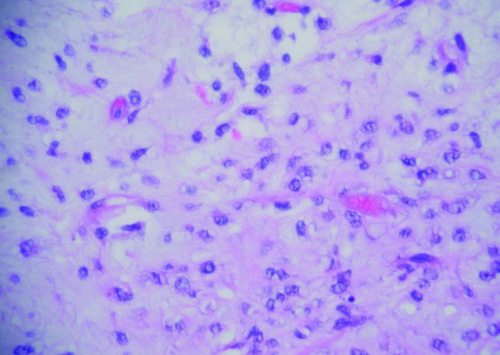
13. Cytogenetic abnormalities identified in this type of neoplasms (Fig. 4.6) include:
a. Abnormalities in chromosome 8q
b. Chromosomal aberrations in 12q
c. Translocation t(12;16)(q13;p11)
d. Deletion of chromosomal region 1p
e. Translocation involving chromosomes 17 and 22
View Answer
13. c.The tumor is composed of lipoblasts in a myxoid background with delicate vasculature and is therefore a myxoid liposarcoma. Translocation t(12;16) is found in >90% of myxoid liposarcoma and leads to fusions of CHOP-FUS genes. In rare cases t(12;22)(q13;q12) has been described with fusion of CHOP-EWS ge
14. The nature of this neoplasm (Fig. 4.7) can be delineated by using any of the following immunohistochemical markers EXCEPT:
a. D2-40
b. Factor VIII
c. Ulex europaeus lectin
d. CD34
e. CD31
View Answer
14. a. CD31, CD34, factor VIII, and Ulex europaeus lectin are endothelial markers that can be used to stain hemangiomas and other tumors. GLUT-1 is another endothelial marker that is specific for infantile hemangiomas. D2-40 stains lymphatic vessels and is not a general endothelial marker.
15. The type of soft tissue sarcoma that develops most commonly in sites of prior radiation in adults is:
a. Fibrosarcoma
c. Ewing sarcoma
d. Pleomorphic malignant fibrous histiocytoma
e. Myxoid malignant fibrous histiocytoma
View Answer
15. d. Malignant fibrous histiocytoma of the pleomorphic type is the most common postradiation sarcoma in adults and occurs after an interval of 10 to 12 years. It can also arise in chronic ulcers and scars. Other conditions can also develop in sites of prior radiation, including reactive spindle cell proliferation, fractures, osteosarcoma, and fibrosarcoma.
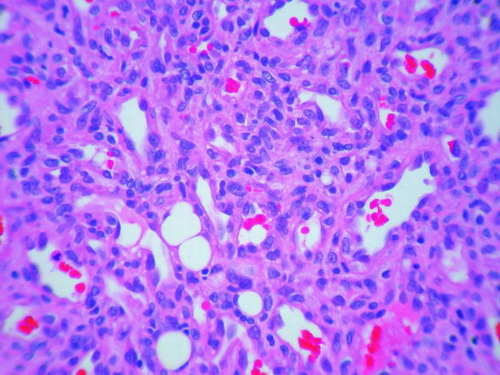
16. These micrographs (Fig. 4.8) are from a section of radiolucent bony lesion in the distal fibula of a 23-year-old woman. The diagnosis is:
a. Unicameral bone cyst
b. Aneurysmal bone cyst
c. Metaphyseal fibrous defect
d. Giant cell tumor
e. Benign fibrohistiocytic tumor
View Answer
16. b. Aneurysmal bone cyst is usually seen in 1 to 20 years of age and occurs mainly in vertebrae and flat bones. Fibroblasts and giant cells in septa that separate cystic spaces are characteristic of aneurysmal bone cyst. On the other hand, solitary or unicameral bone cyst is lined by a slender fibrous membrane that appears different from that of aneurysmal bone cyst.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree