15 Small Intestine Diseases
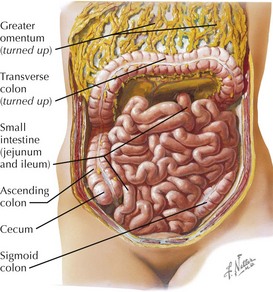
Anatomy of the Small Intestine
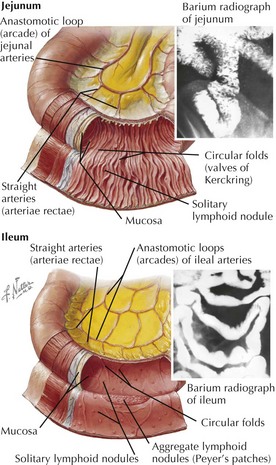
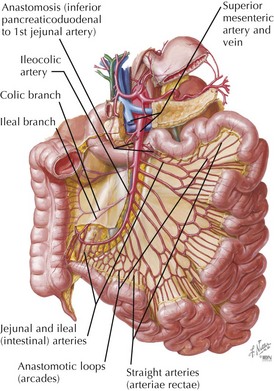
Jejunum
• Locus of maximum water (90%) and nutrient absorption, except for B12, bile acids, iron, and folate
Ileum
• Maximum absorption of nonconjugated bile acids, with conjugated bile acids absorbed in terminal ileum
Microscopic Anatomy
• Submucosa: strongest layer, connective tissue, Meissner’s plexus (parasympathetic ganglion cells and neuronal network)
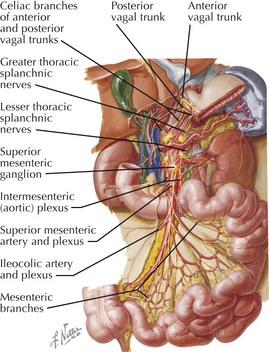
Innervation
• Parasympathetic: vagus
 Preganglionic fibers: posterior branches of right and left vagus distributed through celiac and superior mesenteric plexus
Preganglionic fibers: posterior branches of right and left vagus distributed through celiac and superior mesenteric plexus
 Preganglionic fibers: posterior branches of right and left vagus distributed through celiac and superior mesenteric plexus
Preganglionic fibers: posterior branches of right and left vagus distributed through celiac and superior mesenteric plexus• Sympathetic
 Preganglionic fibers from T8-T10 lateral column distributed via splanchnic nerves to celiac and superior mesenteric ganglia
Preganglionic fibers from T8-T10 lateral column distributed via splanchnic nerves to celiac and superior mesenteric ganglia
 Preganglionic fibers from T8-T10 lateral column distributed via splanchnic nerves to celiac and superior mesenteric ganglia
Preganglionic fibers from T8-T10 lateral column distributed via splanchnic nerves to celiac and superior mesenteric ganglia