36 Skeletal muscle contraction
Microfilamentous structure of skeletal muscle
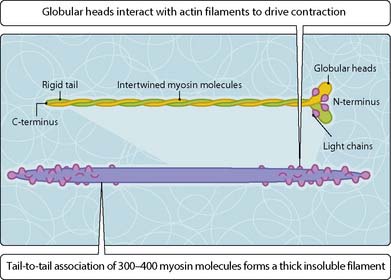
Thick filaments
The core of thick filaments is formed from myosin (Fig. 3.36.1). Myosin molecules are composed of two myosin heavy chains, intertwined to form a rigid tail structure with two head regions at one end. The head regions interact with two light chains each and provide a site for interaction with polymerized actin filaments and a catalytic ATPase domain. Thick filaments are formed by the tail-to-tail association of myosin molecules to form insoluble, rod-like complexes of between 300 and 400 molecules. The head groups protrude to the outside of the structure at both ends and are aligned for optimal interaction with adjacent actin filaments, leaving a central bare zone.