Sjögren Syndrome
Stephen M. Bonsib, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Progressive autoimmune disorder involving exocrine glands, particularly salivary and lacrimal glands
May be primary or a component of other autoimmune disorders
Clinical Issues
Female predominance; age range 45-55
Keratoconjunctivitis and xerostomia most common
Renal disease
Renal failure
Renal tubular acidosis
Proteinuria and hematuria
Risk of non-Hodgkin lymphomas
B-cell lymphoma or Waldenström macroglobulinemia
Cutaneous vasculitis
Cryoglobulins in 30%
Small- to medium-sized vessels
Microscopic Pathology
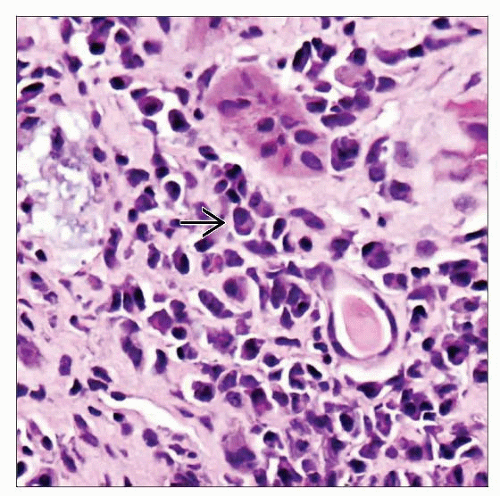
Chronic tubulointerstitial nephritis
Plasma cell-rich infiltrate
Tubular atrophy and interstitial fibrosis
Acute tubulointerstitial nephritis
Tubulitis and edema
Glomerulonephritis
Many forms described
Top Differential Diagnoses
Primary SS vs. association with other autoimmune disorder
Allergic or other interstitial nephritis such as sarcoid
IgG4-related systemic disease
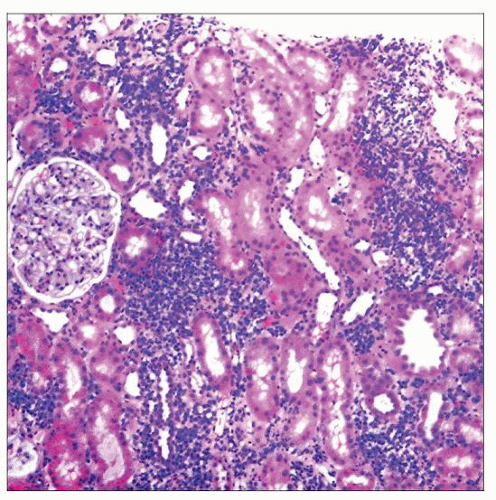 Renal biopsy in Sjögren syndrome typically shows a patchy but heavy interstitial infiltrate. The glomeruli are usually normal. The infiltrate forms broad sheets of cells that separate the tubules. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Sjögren syndrome (SS)
Synonyms
Sicca syndrome
Definitions
Autoimmune disorder involving exocrine glands, particularly salivary and lacrimal glands
May be primary or a component of other autoimmune disorders
Rheumatoid arthritis in 50%
Systemic sclerosis in 5%
Systemic lupus erythematosus in 5%
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Etiology Not Clear
May be multifactorial
Initiation by an exogenous factor, possibly viral
Epstein-Barr virus implicated
Genetic predisposition
Lymphoplasmacytic inflammation with atrophy of eccrine, salivary, and lacrimal glands
T-lymphocyte response
B-lymphocyte hyper-reactivity
Autoantibodies: Rheumatoid factor (RF), SS-A (Ro) and SS-B (La)
Injury to salivary gland epithelium
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Age
45-55 years
Gender
Female predominance (F: M = 9:1)
Presentation
Renal disease ˜ 5%
Tubulointerstitial disease
Distal renal tubular acidosis 70-80%
Renal failure 25-30%
Tubular proteinuria 20%
Hypercalcuria, occasionally hypokalemia
Fanconi syndrome (rare)
Glomerulonephritis 5-15%
Proteinuria &/or hematuria &/or renal failure
Keratoconjunctivitis (dry eyes) > 95%
Xerostomia (dry mouth) > 95%
Cutaneous vasculitis 10-30%
Associated with cryoglobulins in 30%
Small to medium-sized vessels
Peripheral neuropathy ˜ 10%
Interstitial lung disease ˜ 10%
Lymphoma 40x increased risk
B-cell lymphoma or Waldenström macroglobulinemia
Laboratory Tests
50-90% have SS-A antibodies
ANA, anti-SS-B, and RF often positive
Hypergammaglobulinemia
Organ-specific antibodies
Thyroid microsome
Thyroglobulin
Salivary duct epithelium
Gastric parietal cells
Low C4, C3 (9%)
Treatment
Immunosuppression: Corticosteroids, Rituximab
Prognosis
Tubulointerstitial disease an early manifestation
Glomerulonephritis develops later
Renal function improves with treatment in most
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree