Signet Ring Cell Carcinoma
Key Facts
Terminology
Synonym: Adenocarcinoma with signet ring cells
Definition
Non-small cell carcinoma with signet ring cells similar to those described in gastrointestinal tract
Clinical Issues
Symptoms
Chest pain
Shortness of breath
Weight loss
Cough
Treatment
Lobectomy
Chemotherapy &/or radiation depending on clinical setting
Prognosis
Aggressive behavior
Macroscopic Features
1 to > 5 cm in greatest dimension
May have central or peripheral location
Microscopic Pathology
Tumor should be at least 75% signet cell component
Predominant pattern/injury type
Acinar
Diffuse
Top Differential Diagnoses
Metastatic signet ring cell carcinoma
Gastrointestinal, breast, and ovarian origin
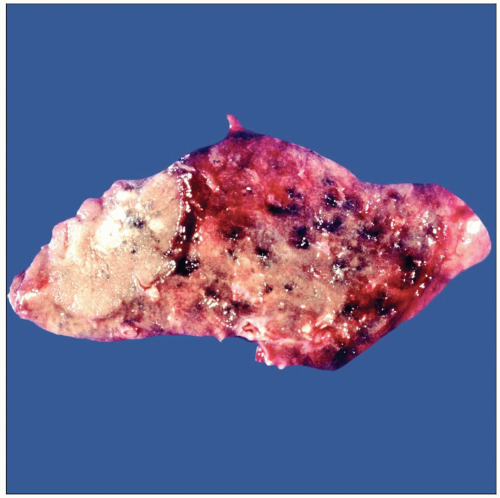 Gross photograph shows a signet ring cell carcinoma. The mass is well defined but not encapsulated. The surface is tan and fairly homogeneous. |
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Adenocarcinoma with signet ring cells
Definitions
Non-small cell carcinoma with signet ring cells similar to those described in gastrointestinal tract
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Etiology
Signet ring cell carcinoma appears to be closely related to bronchial cell-type adenocarcinoma
Bronchial glands may be the site of origin for these tumors
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Primary signet ring cell carcinomas of lung are rare
There is no definitive data on the epidemiology of this tumor
Age
Individuals between 30-70 years old
Like conventional adenocarcinomas, signet ring cell carcinomas are more common in 6th and 7th decades of life
Gender
No gender predilection
Site
No apparent predilection for any side or any lung segment
Presentation
Chest pain
Shortness of breath
Cough
Weight loss
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Lobectomy
Adjuvant therapy
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy depending on clinical and pathological staging
Prognosis
Aggressive behavior
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
1 to > 5 cm in greatest dimension
May have central or peripheral location
Soft consistency, light tan, ± hemorrhage &/or necrosis
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Tumor should be at least 75% signet cell component
Predominant Pattern/Injury Type
Acinar
Diffuse
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree




