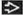Sclerosing Hemangioma (Pneumocytoma)
Key Facts
Terminology
Pneumocytoma
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Tumor appears to have pneumocytic differentiation, yet histogenesis remains unclear
Clinical Issues
Incidence
More common among women
Tumor is more common in 4th and 5th decade of life
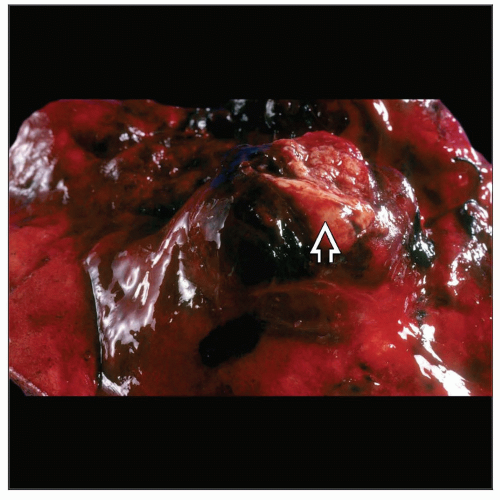
Macroscopic Features
Well-circumscribed but not encapsulated
More often peripheral tumor
Rarely central tumor
Microscopic Pathology
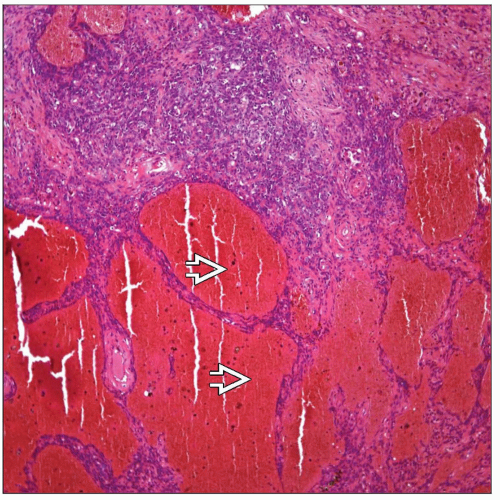
Biphasic
Solid
Papillary
Sclerotic
Hemorrhagic
Combination of patterns more often present in same tumor
Top Differential Diagnoses
Papillary carcinoma
SH lacks nuclear atypia &/or increased mitotic activity
Presence of biphasic cellular population characteristic of SH
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Sclerosing hemangioma (SH)
Synonyms
Pneumocytoma
Definitions
Benign neoplasm of pneumocyte derivation
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Histogenesis
Tumor appears to have pneumocytic differentiation, yet histogenesis remains unclear
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Tumor of rare occurrence
Age
4th or 5th decade of life
Gender
More common among women
Presentation
Asymptomatic
Cough
Chest pain
Hemoptysis
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Complete surgical resection
Prognosis
Excellent
In unusual cases, tumor metastasizes to lymph nodes
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Well-circumscribed but not encapsulated
More often peripheral tumor; rarely central location
Size
1-8 cm in diameter
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Solid
Papillary
Sclerotic
Hemorrhagic
Combination of patterns often present in same tumor
Cytologic Features
Small cells with hobnail nuclei lining papillary structures
Monotonous population of round/polyclonal cells with clear cytoplasm in solid areas
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Papillary Carcinoma
Marked nuclear atypia &/or increased mitotic activity
Presence of biphasic cellular population is characteristic of SH
Carcinoma and SH show positive staining for similar markers, including keratin and TTF-1
Increased proliferative activity (↑ Ki-67 stain)
Mesothelioma
Would be unusual for mesothelioma to present with intrapulmonary mass
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree