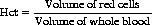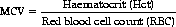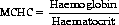Chapter 41 Scientific tests
Blood Tests (Table 41.1)
Table 41.1 Normal adult ranges in common diagnostic tests.
| Test | Normal Range | |
| Males | Females | |
| FULL BLOOD COUNT | ||
| Red blood cells | 4.5–6.5 1012/L | 3.8–5.0 1012/L |
| Haemoglobin | 13–18 g/100 mL | 11.5–16.5 g/100 mL |
| Hct | 45–52% | 37–48% |
| MCV | 80–96 femtoL | 80–96 femtoL |
| MCH | 27–32 pg | 27–32 pg |
| MCHC | 32–36 g/dL | 32–36 g/dL |
| RDW | 11–15% | 11–15% |
| White blood cell count | 4–11 109/L | 4–11 109/L |
| Neutrophils | 2.0–7.5 109/L | 2.0–7.5 109/L |
| Lymphocytes | 1.3–4.0 109/L | 1.3–4.0 109/L |
| Monocytes | 0.2–0.8 109/L | 0.2–0.8 109/L |
| Eosinophils | 0.04–0.44 109/L | 0.04–0.44 109/L |
| Basophils | 0.0–0.109/L | 0.0–0.109/L |
| Platelets | 150–440 109/L | 150–440 109/L |
| AUTOMATED WHITE CELL DIFFERENTIAL | ||
| Segmented neutrophils | 34–75% | 34–75% |
| Band neutrophils | 8% | 8% |
| Lymphocytes | 12–50% | 12–50% |
| Monocytes | 3–15% | 3–15% |
| Eosinophils | 5% | 5% |
| Basophils | 3% | 3% |
| Prothrombin time | 10–15 s | 10–15 s |
| LIVER FUNCTION TESTS | ||
| Bilirubin | 0–21 micromol/L | 0–21 micromol/L |
| Serum alkaline phosphatase | 20–125 iu/L | 20–125 iu/L |
| ALT/SGPT | 0–40 iu/L | 0–40 iu/L |
| ALT/SGOT | 0–48 /L | 0–48 IU/L |
| GGT | 0–45 IU/L | 0–45 IU/L |
| Total serum protein | 59–82 g/L | 59–82 g/L |
| Blood Lipids | ||
| Total cholesterol | >200 mg/dL | >200 mg/dL |
| HDL | <37 mg/dL | <47 mg/dL |
| LDL | >130 mg/dL | >130 mg/dL |
| Triglycerides | >150 mg/dL | >150 mg/dL |
| Ferritin | 18–270 ng/mL | 18–160 ng/mL |
| Fasting glucose | 60–109 mg/dL | 60–109 mg/dL |
| UREA AND ELECTROLYTES | ||
| Serum sodium | 133–145 mmol/L | 133–145 mmol/L |
| Serum potassium | 3.5–5.3 mmol/L | 3.5–5.3 mmol/L |
| Serum urea | 2.5–6.6 mmol/L | 2.5–6.6 mmol/L |
| Serum creatinine | 45–110 lmol/L | 45–110 lmol/L |
| Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) | >15 mm/h | >20 mm/h |
| Rheumatoid factor | 0–35 IU/mL | 0–35 IU/mL |
| HORMONAL LEVELS | ||
| Serum TSH | 0.3–3 mIU/L | 0.3–3 mIU/L |
| Serum thyroxine T4 (protein bound) | 4.6–12 lg/dL | 4.6–12 lg/dL |
| Free T4 (FT4) | 0.7–1.9 ng/dL | 0.7–1.9 ng/dL |
| Serum triiodothyronine (protein bound) | 80–180 ng/dL | 80–180 ng/dL |
| Free T3 (FT3) | 230–619 pg/d | 230–619 pg/d |
| Serum prolactin | N/A | 0 to 20 ng/mL |
| Serum LH | N/A | 5–20 mIU/mL |
| Serum FSH | N/A | 5 –30 mIU/mL |
| Serum FSH after menopause | N/A | 50–100 mIU/mL |
| KEY VITAMIN AND METABOLITES | ||
| Serum B12 | 150–600 pmol/L | 150–600 pmol/L |
| Red cell folate | 360–1400 nmol/L | 360–1400 nmol/L |
| Homocysteine | 5–15 lmol/L | 5–15 lmol/L |
| METALS | ||
| Copper | >20 mg/dL | >20 mg/dL |
| Urinary copper | <100 μg/24h | <100 μg/24h |
Full Blood Count
This is performed if there is:
Babies under 1 year and pregnant women can also be screened this way.
Haematocrit (Hct)
• If raised, can indicate reduced plasma volume, possibly due to dehydration, e.g. drug (diuretic) or alcohol induced. Might also indicate increased red cell mass due to certain types of tumours.
• Mean Cell (Corpuscular) Volume (MCV)
• Low in microcytic anaemia, found in iron-deficient anaemia (see Chapter 28 ‘Blood disorders’, p. 209).
• High in macrocytic anaemia, found in pernicious anaemia (see Chapter 28 ‘Blood disorders’, p. 210).
• Mean Corpuscular Cell Haemoglobin Concentration (MCHC)
• Normal in macrocytic (normochromic) anaemias: this is because although the cell size is larger than normal the amount of haemoglobin is high therefore making the concentration normal:
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree