Schistosomiasis
Key Facts
Terminology
Synonym
Bilharziasis
Definition
Infection caused by Trematoda (flukes)
Etiology/Pathogenesis
3 most common types that affect humans are
Schistosoma haematobium (urinary tract)
Schistosoma mansoni (intestinal tract)
Schistosoma japonicum (intestinal tract)
Pathogenesis
Snails are intermediate host
Schistosoma eggs travel via the portal-systemic collateral veins to the lung
Clinical Issues
Acute phase
Chronic phase
Laboratory findings
Eosinophilia
Possible false-positive HIV test
Treatment
Good if treated early and patient not immunocompromised
Can be fatal in some cases
Top Differential Diagnoses
Fungal granulomatous infection
Pulmonary tuberculosis
Pulmonary hypertension
Bacterial bronchopneumonia
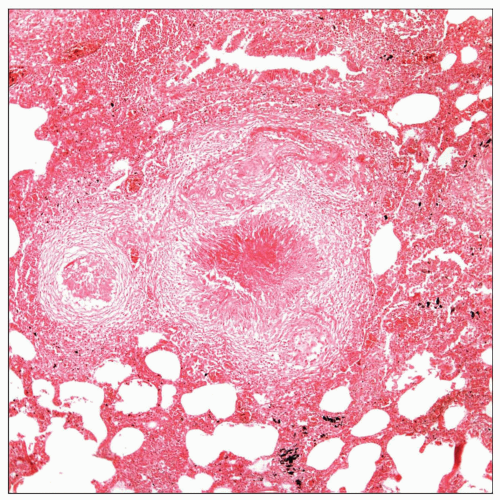 Lung parenchyma with an easily identifiable granulomatous reaction shows that the center of the granulomas contain necrosis and hemorrhage. These changes can be seen in other infections as well. |
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Bilharziasis
Definitions
Infection caused by Trematoda (flukes)
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Infectious Agents
3 most common types affecting humans are
Schistosoma haematobium (urinary tract)
Schistosoma mansoni (intestinal tract)
Schistosoma japonicum (intestinal tract)
Snails are intermediate host
Pathogenesis in Pulmonary Schistosomiasis
Schistosoma eggs travel via the portal-systemic collateral veins to the lung
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Approximately 10% worldwide
Age
Any age group can potentially be affected
Gender
No gender predilection
Ethnicity
No ethnic predilection
Presentation
Acute phase
Fever
Cough
Asthma-like symptoms
Urticaria
Diarrhea
Hepatomegaly
Splenomegaly
Lymphadenopathy
Chronic phase
Acute symptoms subside over a period of weeks
Patients may be asymptomatic
Laboratory Tests
Eosinophilia
Possible false-positive HIV test
Treatment
Drugs
Praziquantel (all types of Schistosoma)
Oxamniquine (S. mansoni)
Metrifonate (S. haematobium)
Prognosis
Good if treated early and patients not immunocompromised
Can follow aggressive course in immunocompromised individuals
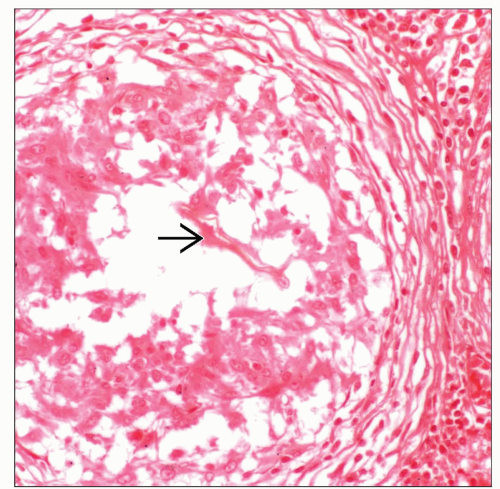
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Granulomatous reaction
Granulomatous endarteritis
Thickening of pulmonary vasculature
Schistosoma eggs deposited in arterioles
Acute inflammatory reaction
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Fungal Granulomatous Infection
Presence of fungal organisms demonstrated by fungal stains
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree