Sarcoidosis
Xin Gu, MD
Key Facts
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Unclear etiology; disordered immune regulation
Renal dysfunction related to nature and extent of involvement
Clinical Issues
More common in African-Americans than whites
Involves multiple organs
Isolated renal sarcoidosis rarely occurs
Elevated calcium and ACE levels help diagnosis
Image Findings
Hilar lymphadenopathy
Macroscopic Features
Usually unremarkable
Microscopic Pathology
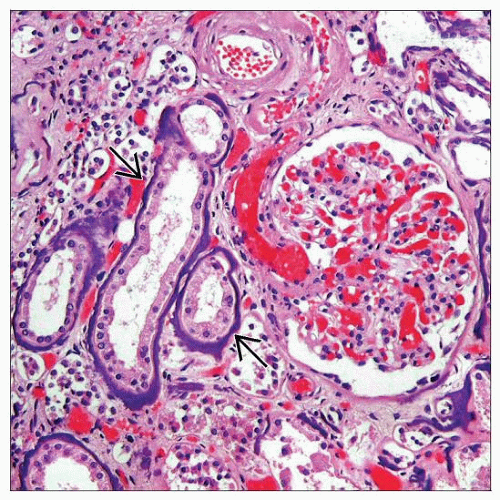
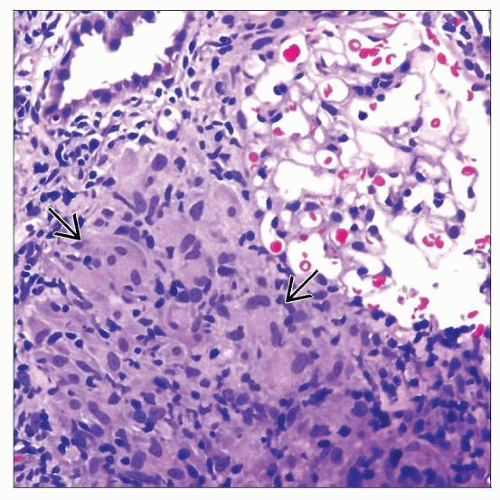
Well-formed noncaseating granulomas
Interstitial fibrosis in chronic recurrent renal sarcoidosis
Glomerulonephritis rarely occurs
Top Differential Diagnoses
Allergic (drug-induced) tubulointerstitial nephritis
Most common
Granulomas less distinct, often with eosinophils
Granulomatous infections
Caseation may be present
Special stains for organisms required
Granulomatous vasculitis
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener)
Giant cell arteritis
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Systemic granulomatous disease
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Etiology Unclear
Possibly multifactorial
Disordered immune regulation affecting T cells and histiocytes leading to tissue injury
Inflammatory cytokines stimulate synthesis of 1,25 OH vitamin-D3 leading to hypercalcemia
Genetic susceptibility &/or environmental factors
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
1-40 per 100,000 population
Age
Most common in 2nd-4th decades
Gender
More common in males than females
Ethnicity
3.5-10x higher in African-Americans than whites
Presentation
Nonspecific systemic symptoms
Lymphadenopathy
Cough, dyspnea, fever
Renal involvement in 15-45% of patients
Tubular dysfunction due to hypercalcemia
Urine concentration defect with polyuria
Acute or chronic renal failure
Hydronephrosis from retroperitoneal lymphadenopathy
Laboratory Tests
Hypercalcemia (50-60%)
Elevated angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) level
Azotemia
Hematuria &/or proteinuria, low grade to nephrotic
Treatment
Drugs
Steroids
Prognosis
Usually good, most patients respond to steroids
Worse outcome in African-Americans and elderly
Recurrent or resistant disease
Acute or chronic renal failure
Death
IMAGE FINDINGS
Radiographic Findings
Mediastinal lymphadenopathy
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features