Rosai-Dorfman Disease
Key Facts
Terminology
Synonym: Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy (SHML)
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Unknown
Possible infectious origin
Possible immunologic response
Clinical Issues
R-D disease is unusual tumoral condition more commonly seen in lymph nodes
May appear in extranodal sites in ˜ 20% of cases
Respiratory system is most unusual site of occurrence
Surgical resection is treatment of choice
Chemotherapy can be used in more severe and extensive cases
However, its use has not shown meaningful results
Prognosis
May follow nonaggressive course
In a few cases, fatal course may be observed, but that is unusual
Some patients may live with persistent disease
Number of cases involving lung is too small to make definitive conclusions
Top Differential Diagnoses
Infectious process
Histochemical stains for fungi and acid-fast bacilli are negative
Erdheim-Chester disease (E-C disease)
Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH)
Juvenile xanthogranuloma (JXG)
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Rosai-Dorfman (R-D) disease
Synonyms
Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy (SHML)
Definitions
Histiocytic proliferation primarily affecting lymph nodes
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Etiology
Unknown
Possible infectious origin
Possible immunologic response
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Unusual tumoral condition more commonly seen in lymph nodes
May appear in extranodal sites in approximately 20% of cases
Respiratory system is most unusual site of occurrence
Age
May occur at any age
Cases described in lung have been in adults
Presentation
Cough
Shortness of breath
Chest pain
Treatment
Surgical resection is treatment of choice
Chemotherapy can be used in more severe and extensive cases
However, its use has not shown meaningful results
Prognosis
Generally good
In a few cases, fatal course may be seen, but that is unusual
Some patients may live with persistent disease
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Pulmonary mass indistinguishable from bronchogenic carcinoma
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
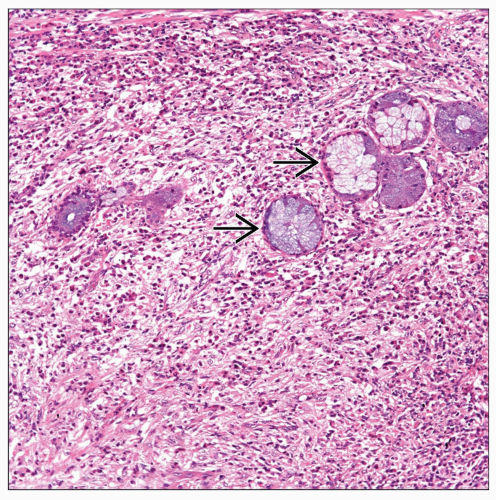
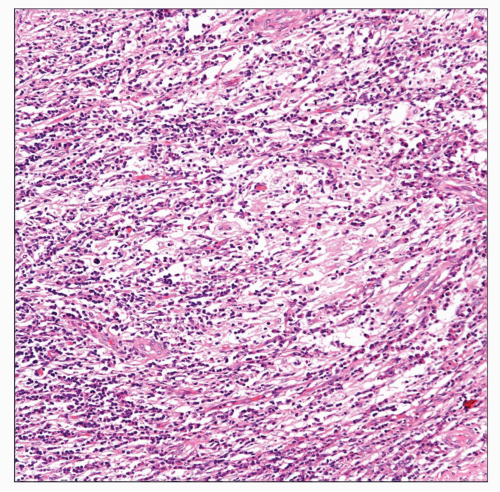
Diffuse proliferation of large histiocytes
Presence of histiocytes engulfing lymphocytes (emperipolesis)
Presence of inflammatory reaction, namely plasma cells
When lung is affected, lymph nodes may also be involved
Predominant Pattern/Injury Type
Sheets
Predominant Cell/Compartment Type
Histiocyte/macrophage
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Infectious Process
Histochemical stains for fungi and acid-fast bacilli are negative
Erdheim-Chester (E-C) Disease
May show similar immunophenotype
Shows histiocytes of normal size, while R-D disease shows large histiocytes
Absence of emperipolesis in E-C disease
Different growth pattern, namely in septum and pleura
Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis (LCH)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree