Rhabdomyosarcoma
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
Anterior mediastinum
Cough
Chest pain
Dyspnea
Pleural effusion
Highly aggressive tumors with short survival
Microscopic Pathology
Sheets of “small round blue cells” with hyperchromatic nuclei and scant eosinophilic cytoplasm
Spindle cell variant of embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma is composed of fascicular proliferation of atypical spindle cells against myxoid stroma
Artifactual clefting of nests of small blue cells from periphery results in striking “alveolar” pattern
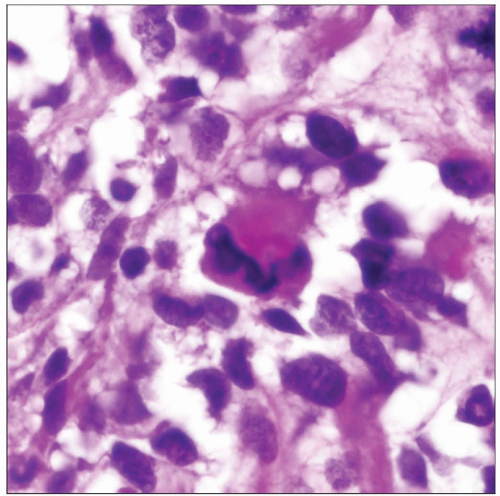
Scattered multinucleated tumor cells with large hyperchromatic nuclei are seen admixed with small blue tumor cells
Bizarre atypical cells with large, pleomorphic, and irregular nuclei are seen in pleomorphic variant of rhabdomyosarcoma
Ancillary Tests
Tumor cells are positive for desmin, Myo-D1, and myogenin
Tumor cells may aberrantly express cytokeratin, NSE, and S100 protein
Electron microscopy will show thick and thin filaments with Z-bands
PAX3/FKHR and PAX7/FKHR fusion product can be detected by FISH in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma
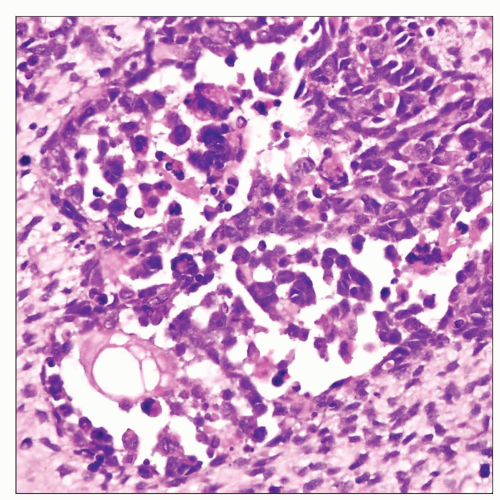 Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma of the anterior mediastinum shows sheets of primitive small round blue cells with prominent retraction artifact resulting in an “alveolar” appearance. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS)
Definitions
Primary malignant neoplasm of mediastinum showing features of striated muscle differentiation
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Pathogenesis
Pure cases may arise from totipotential stem cells within mediastinal soft tissue
Cases associated with teratomatous elements may arise from somatic transformation of germ cells
Cases associated with thymic carcinosarcomatous elements may arise from native thymic myoid cells
CLINICAL ISSUES
Site
Anterior mediastinum
Presentation
Cough
Chest pain
Dyspnea
Pleural effusion
Mostly affects young adults (mean: 23 years)
Treatment
Surgical excision
Adjuvant chemotherapy and radiation therapy
Prognosis
Highly aggressive tumors with short survival time
Rapid recurrence and metastases generally within 1st 6 months after diagnosis
Metastases most often involve lymph nodes but may also involve lung, pleura, bone, and abdominal viscera
IMAGE FINDINGS
General Features
Solid, unencapsulated expansile lesion with poorly defined, infiltrative borders
CT scans show large homogeneous mass displacing midline structures with pleural effusion
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Firm, poorly circumscribed, and infiltrative mass
Homogeneous, tan-gray cut surface
Areas of hemorrhage and necrosis
Size
4-12 cm
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Tumors may appear de novo in pure form, or may be associated with germ cell, teratomatous, or carcinomatous elements
Pure, de novo tumors may show varied histology
Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma
Sheets of “small round blue cells” with hyperchromatic nuclei and scant eosinophilic cytoplasm
Scattered immature rhabdomyoblasts characterized by comma-shaped cells with small, dark nuclei and bright pink rim of cytoplasm
Spindle cell variant of embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma is composed of atypical spindle cells set against myxoid stroma
Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma
Solid sheets of “small round blue cells” supported by delicate fibrovascular stroma
Artifactual clefting of nests of small blue cells from periphery results in striking “alveolar” pattern
Scattered multinucleated tumor cells with large hyperchromatic nuclei are seen admixed with small blue tumor cells
Pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma
Bizarre atypical cells with large, pleomorphic, and irregular nuclei surrounded by abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm
Cells may show slender, tapering cytoplasmic processes resembling racquet cells
Only rarely will cells display cytoplasmic cross-striations
Cytologic Features
Small round blue cells show primitive cytologic appearance with hyperchromatic nuclei devoid of nuclear detail
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree