Respiratory Bronchiolitis
Key Facts
Terminology
Respiratory bronchiolitis-interstitial lung disease (RB-ILD)
Synonym: Smoker’s bronchiolitis
Mild form of interstitial lung disease
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Closely associated with smoking history
Occupational exposure to fumes
Clinical Issues
Symptoms
Cough
Dyspnea
Wheezing
Flue-like symptoms
Laboratory findings
There are no specific laboratory findings for RB
Pulmonary function tests may be normal
Treatment
Cessation of smoking
Corticosteroids
Top Differential Diagnoses
Desquamative interstitial pneumonitis (DIP)
Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH)
Usual interstitial pneumonitis (UIP)
Diagnostic Checklist
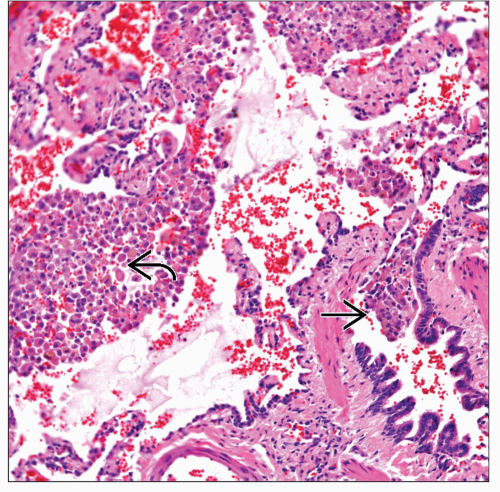
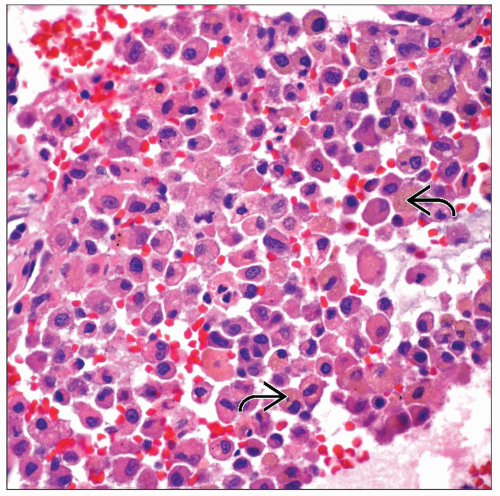
Collections of pigmented macrophages in lumens of airways
Collections of intraalveolar macrophages around small airways
Absence of marked interstitial fibrosis
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Respiratory bronchiolitis-interstitial lung disease (RB-ILD)
Synonyms
Smoker’s bronchiolitis
Small airway disease
Definitions
Mild form of interstitial lung disease
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Environmental Exposure
Closely associated with smoking history
Occupational exposure to fumes
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
No hard data on incidence
Age
Generally in adults
Gender
No gender predilection
Ethnicity
No ethnic preference
Site
Small airways of lung parenchyma
Presentation
Cough
Dyspnea
Wheezing
Flu-like symptoms
Laboratory Tests
There are no specific laboratory findings for RB
Pulmonary function tests may be normal or show only minimal changes
Treatment
Drugs
Corticosteroids
Cessation of smoking
Prognosis
Very good prognosis
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Most of the time, diagnosis of RB-ILD is made during open lung biopsy
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Pigmented macrophages in lumens of airway
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree