Radiocephalic (Cimino–Brescia) arteriovenous fistula at the wrist; brachiocephalic or first-stage brachiobasilic fistula in the antecubital fossa.
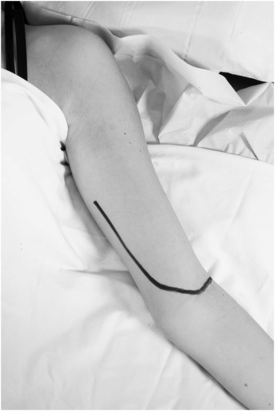
Second-stage brachiobasilic arteriovenous fistula, also known as a basilic vein transposition and superficialisation; palpate for a possible prosthetic graft (PTFE or Dacron) in case the fistula has been revised.
What are the features of a transplanted kidney?
Renal transplants are most commonly placed in the right or left iliac fossa.
Non-functioning native kidneys are usually left in situ. Consequently, nephrectomy scars will not always be present in patients with end-stage renal failure. Indications for nephrectomy in patients with renal failure include infected polycystic kidneys or renal carcinoma.
Beware of small incisions used in laparoscopic nephrectomy.
A smooth, non-tender, kidney-shaped, dull mass may be palpable in the iliac fossa.
What investigation may be necessary in patients planning to have a fistula formed?
A bedside/outpatient ultrasound scan may be performed to assess the position and calibre of the peripheral arteries and veins.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


