Refractory Cytopenia with Unilineage Dysplasia
Carla S. Wilson, MD, PhD
Key Facts
Terminology
MDS disorders characterized by unicytopenia or bicytopenia plus dysplasia
Can further specify based on lineage
Refractory anemia is most common
Refractory neutropenia
Refractory thrombocytopenia
Dysplasia isolated to a single lineage
Involves ≥ 10% of cells in affected cell lineage
Usually of same lineage as cytopenia
Clinical Issues
Older adults; median age: 65-70 years
Low-grade MDS
Prolonged and indolent course
May require transfusions or erythropoietin therapy
Only rare cases progress to acute myeloid leukemia
Microscopic Pathology
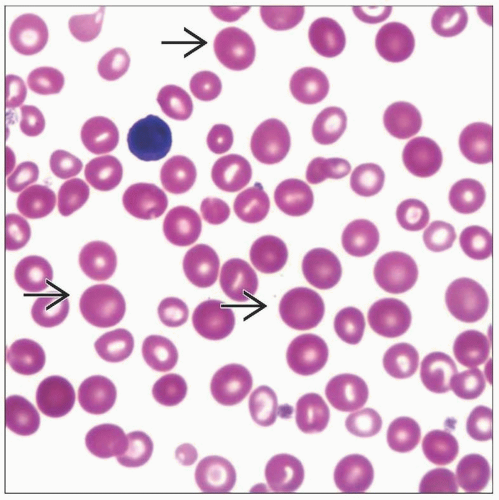
Peripheral blood
< 1% blasts
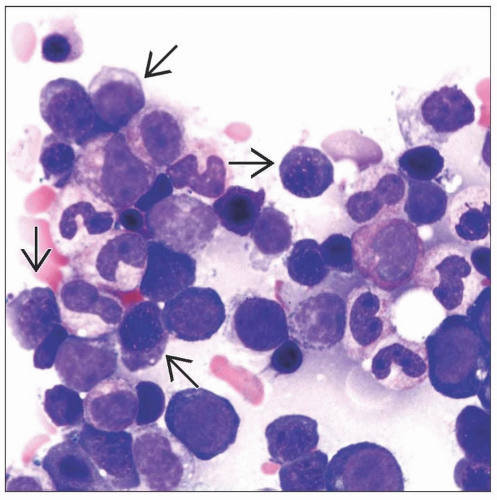
Bone marrow
< 5% blasts
Unilineage dysplasia
Diagnostic Checklist
May be difficult to diagnose based on morphology alone
Helpful if clonal cytogenetic abnormality (found in ˜ 50% of cases)
If normal karyotype, need to exclude nonclonal causes for cytopenia and dysplasia
Evaluate for at least 6 months before establishing diagnosis
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Refractory cytopenia with unilineage dysplasia (RCUD)
Definitions
Group of myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) that present with RCUD
Refractory anemia (RA) is most common in adults
Refractory neutropenia is rare
Refractory thrombocytopenia is rare
Bicytopenia may be present but not pancytopenia
Unilineage dysplasia involves ≥ 10% of cells in affected cell lineage
Dysplasia is usually of same lineage as cytopenia
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Environmental Exposure
Chemicals or solvents such as benzene
Toxins such as cigarette smoke
Acquired Disorder
Clonal hematopoietic stem cell disease
Increased apoptosis with ineffective hematopoiesis
Immune dysregulation plays a role
Allows growth of dysplastic clone
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
10-20% of MDS
Age
Older adults, median age 65-70 years
Gender
Similar incidence for males and females
Presentation
Most common presentation is macrocytic or normochromic normocytic anemia
Symptoms relate to type of cytopenia
Anemia
Fatigue, dizziness, headaches, palpitations
Neutropenia
Increased infections
Thrombocytopenia
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree