Refractory Anemia with Excess Blasts
Carla S. Wilson, MD, PhD
Key Facts
Terminology
MDS with increased blasts or Auer rods
RAEB-1
2-4% blasts in peripheral blood or
5-9% blasts in bone marrow
RAEB-2
5-19% blasts in peripheral blood or
10-19% blasts in bone marrow or
Auer rods
Clinical Issues
35-40% of MDS
Most MDS with reticulin fibrosis is RAEB-F
25% 5-year survival rate
Progress to AML at 5 years
25% of RAEB-1 cases
35% (to 50%) of RAEB-2 cases
High-risk MDS
May be treated similarly to AML
Microscopic Pathology
Dysplasia is often more pronounced than for other types of MDS
Ancillary Tests
Cytogenetic analysis is essential
Immunohistochemistry
Architectural abnormalities are common
Flow cytometry
Abnormal maturation patterns common
Top Differential Diagnoses
De novo AML with low blast count
Consider if Auer rods are present
Recovery from bone marrow aplasia
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Refractory anemia with excess blasts (RAEB)
Definitions
Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) with increased blasts or Auer rods
2 categories based on prognosis
RAEB-1
2-4% blasts in peripheral blood or
5-9% blasts in bone marrow
RAEB-2
5-19% blasts in peripheral blood or
10-19% blasts in bone marrow
Auer rods, if present, advance MDS case to RAEB-2
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Disorder
Clonal hematopoietic stem cell disorder
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
35-40% of MDS
15-20% RAEB-1
20% RAEB-2
Associated reticulin fibrosis seen in ˜ 10% of MDS; most are RAEB-F (fibrosis)
Age
Older individuals, primarily > 50 years of age
Presentation
Often seek medical attention for symptoms of anemia
Fatigue, dyspnea, palpitations, headache, dizziness
Other symptoms related to cytopenias
Exaggerated bleeding from thrombocytopenia with platelet dysfunction
Infection secondary to decreased neutrophils and neutrophil dysfunction
Occasional mild hepatomegaly or splenomegaly
Treatment
High-risk MDS
May be treated similarly to acute myeloid leukemia (AML)
Depends partly on tempo of disease progression
Intensive chemotherapy with variety of regimens
RAEB-2 patients who are candidates for stem cell transplantation
Topotecan-cytarabine or idarubicin-cytarabine-based regimens
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Patient must have low comorbidity scores
High upfront treatment-related mortality
May want to delay for low-risk or intermediate-risk patients
Risk of relapse increases if cytogenetics classified as poor risk
Prognosis
25% 5-year survival rate
Patients have progressive bone marrow failure with increasing cytopenias
Die from complications such as bleeding and infections
Subset progresses to AML
25% of RAEB-1 cases at 5 years
35% (to 50%) of RAEB-2 cases at 5 years
Predicted survival based on blast percentage, cytogenetic abnormalities, cytopenias
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Cytologic Features
Peripheral blood
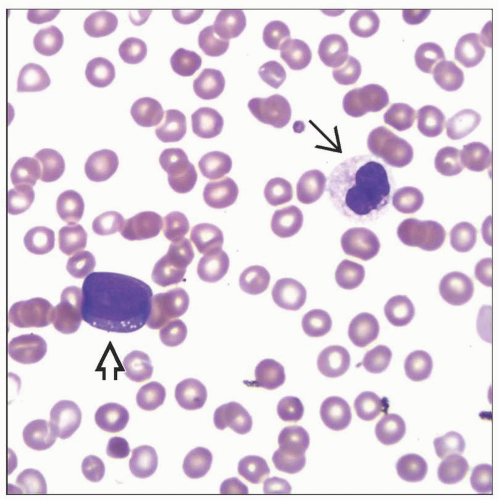
Anemia with anisopoikilocytosis
Neutropenia with dysplastic features
Blasts increased but < 20%
Thrombocytopenia
Giant or hypogranular platelets
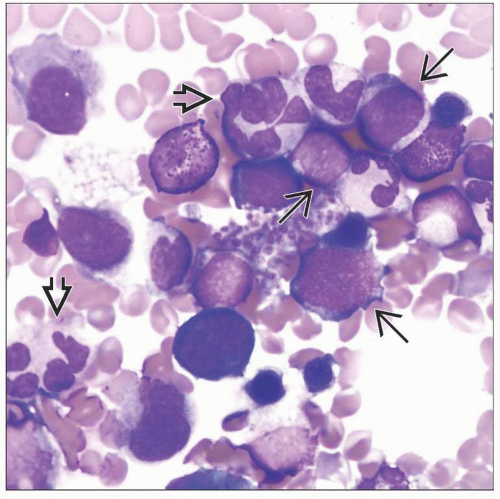
Bone marrow
Usually hypercellular, often multilineage dysplasia
Dysplasia is often (but not always) more pronounced than for other types of MDS
Increased blasts in clusters or aggregates
Erythropoiesis may be increased, variably dysplastic
Colony formation disrupted or abnormally located near paratrabecular areas
Granulopoiesis may be increased, variably dysplastic
Abnormal localization of immature precursors (ALIP) in nonparatrabecular areas

Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree