Chapter 10 Radiology Tools for Abdominal Diagnosis
Radiology and the Competencies
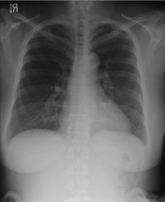
1. Chest Radiograph (PA)
The following mnemonic may be helpful to remind you of what to look for on a chest radiograph:
Specific abnormal findings to look for on the chest x-ray:
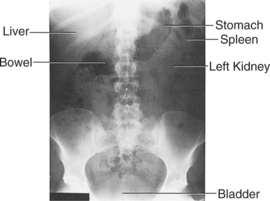
2. Supine Abdominal Radiograph—Normal Anatomy (AP)
When viewing abdominal radiographs, it is important to evaluate for:
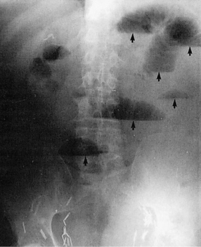
3. Erect Abdominal Film (AP)
Table 10-1 Calcifications Seen on Abdominal X-rays
| Entity | Notes |
|---|---|
| Gallstones | 10% of gallstones are radiopaque. May be incidental finding. |
| Appendicolith | Its presence is associated with appendicitis. |
| Chronic pancreatitis | Multiple calcifications in pancreas. |
| Abdominal aortic aneurysm | Look for calcium in aortic wall. |
| Nephrolithiasis/ureterolithiasis | Stones may be apparent overlying kidney shadow. Ureteral stones may appear anywhere along course of ureter. |
| Gallstone “ileus” | A gallstone large enough to block the ileocecal valve enters the bowel via a biliary enteric fistula from the gallbladder to the duodenum; usually the result of untreated chronic cholecystitis. |
| Uterine fibroids | Calcified fibroids may appear in pelvis. |
| Dermoid cysts | A dermoid is a mature teratoma that may manifest as a calcified “tooth” in pelvis. |
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree