Chapter 12 Purines and pyrimidines
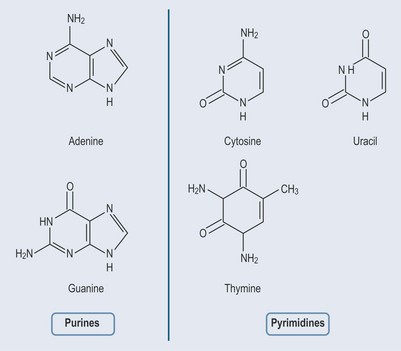
Purines and pyrimidines are known as nitrogenous bases. The two groups have different features (Figure 12.1):
These nitrogenous bases are crucial not only to the storage and transmission of genetic information, but also as a means of storing mobile energy. They can be synthesized in the body from basic components. The degraded bases can be salvaged and reused (see Chapter 37 ‘Metabolic disorders’, p. 295).
Nucleosides and Nucleotides
When a sugar is added to a nitrogenous base, a nucleoside is formed (Figure 12.2).
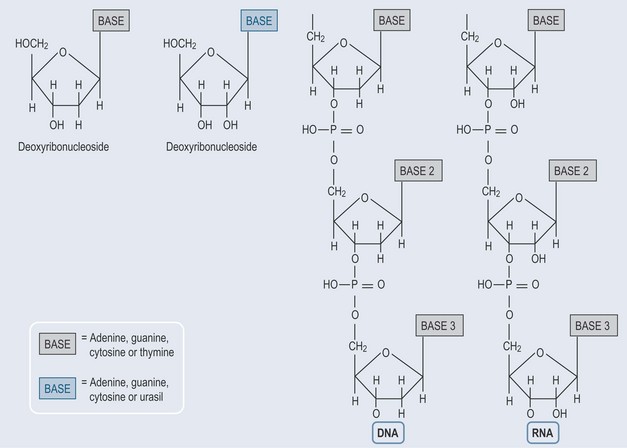
Figure 12.2 The basic structure of nucleosides and their inclusion in the nucleotide structures of RNA and DNA.
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree