Pulmonary Paraganglioma
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
Extremely rare tumor in pulmonary location
Solitary, peripheral “coin” lesion
Central, endobronchial lesion
Microscopic Pathology
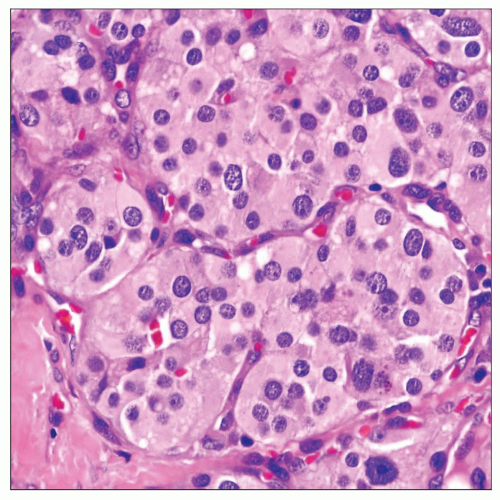
Principal feature is “endocrine” or “organoid” growth pattern
Most common pattern of growth is discrete nests of tumor cells separated by fibrovascular septa (zellballen pattern)
Large round or polygonal cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm
Large round cells with abundant clear cytoplasm
Elongated cells with spindle nuclei and abundant cytoplasm
Oncocytic cells with abundant granular eosinophilic cytoplasm
Foci containing cells with macronuclei or bizarre nuclei but devoid of mitotic activity are common
Ancillary Tests
Strong positivity of tumor cells for neuroendocrine-associated markers, including chromogranin, synaptophysin, and CD56
S100 protein-positive sustentacular cells are seen surrounding the tumor cell “nests”
Diagnostic Checklist
Histologic features are notoriously unreliable for predicting biologic behavior
Most common differential diagnosis is with pulmonary “carcinoid” tumor
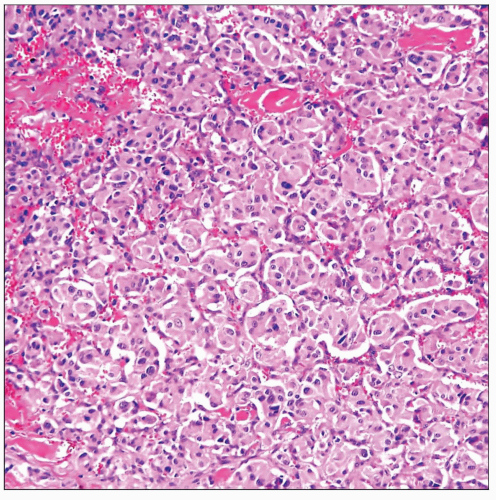 Scanning magnification of pulmonary paraganglioma shows characteristic neuroendocrine architecture (zellballen pattern) of these tumors composed of discrete “nests” of epithelioid cells. |
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Pulmonary chemodectoma, extraadrenal paraganglioma
Definitions
Primary neuroendocrine lung neoplasm derived from ectopic paraganglionic elements
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Extremely rare tumor in pulmonary location
Age
Middle-aged adults (40-50 years of age)
Gender
Male predominance
Presentation
Solitary, peripheral “coin” lesion
Central, endobronchial lesion
Endocrine symptoms
Hypertension
Increased serum norepinephrine
Cushing syndrome
Endobronchial lesion may present with obstructive symptoms
Cough
Wheezing
Dyspnea
Stridor
Treatment
Surgical excision
Prognosis
Majority of reported cases have been benign
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Well-circumscribed intraparenchymatous nodule
Smooth, well-circumscribed endobronchial lesion
Size
1-3 cm in greatest diameter