Pulmonary Meningioma
Key Facts
Terminology
Primary intrapulmonary meningothelial neoplasm
Clinical Issues
Cough
Asymptomatic
Lobectomy
Wedge excision in small tumors
Good prognosis in conventional cases
Aggressive behavior in malignant tumors
Macroscopic Features
Varying tumor size: 1-6 cm
Well-circumscribed
Microscopic Pathology
Spindle (fibrous meningioma)
Meningothelial (transitional meningioma)
Presence of psammoma bodies
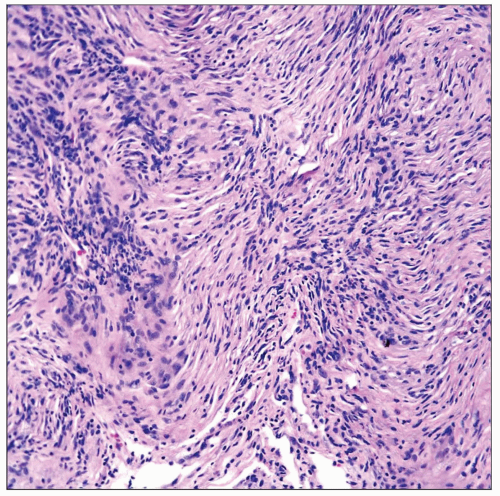
Whorled pattern
Spindle cells arranged in vague storiform pattern
Ancillary Tests
EMA
KERATIN-PAN
CD34
TTF-1
Top Differential Diagnoses
Well-differentiated neuroendocrine carcinoma (carcinoid)
Malignant meningioma
Meningothelial-like nodule
Meningotheliomatosis
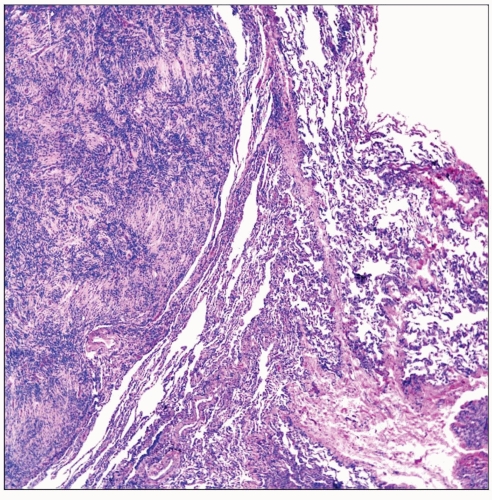 Hematoxylin & eosin section shows a well-circumscribed intraparenchymal tumor replacing the normal lung parenchyma. |
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Primary intrapulmonary meningothelial neoplasm
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Etiology
Previous meningothelial-like nodules
In cases where pulmonary meningioma is associated with other small lesions of same histology
Pluripotential cells
Cells capable of undergoing differentiation toward meningothelial cells
Heterotopic embryonic rests
Possible ectopic neuroectodermal tissue in lung
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Primary pulmonary meningiomas are exceedingly rare
Only a few short series of cases have been reported
Age
More common in adults
Gender
No gender predilection for pulmonary meningiomas
Presentation
Asymptomatic
Cough
Chest pain
Shortness of breath
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Lobectomy
Wedge excision in small tumors
Prognosis
Generally excellent prognosis
Aggressive behavior in malignant tumors
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Varying tumor size: 1-6 cm
Well-circumscribed tumor lesion
Cut surface is white and homogeneous
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Presence of psammoma bodies
Whorled pattern of growth
Spindle cells arranged in vague storiform pattern
Focal areas with presence of foamy macrophages
Mixture of meningothelial “transitional” and spindle cells
Predominant Pattern/Injury Type
Whorled
Predominant Cell/Compartment Type
Meningothelial
Spindle
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Well-differentiated Neuroendocrine Carcinoma (Carcinoid)
Carcinoid usually does not show characteristic whorled pattern
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree