Pulmonary BALT Hyperplasia
Key Facts
Terminology
Polyclonal proliferation of small lymphocytes arising within lung parenchyma
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Commonly associated with underlying autoimmune disorders such as Sjögren syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, and collagen vascular diseases
Associated with viral infection, including HIV and Epstein-Barr virus
Associated with immunodeficiency, including common variable immunodeficiency, AIDS, and bone marrow transplants
Clinical Issues
Mostly asymptomatic; discovered incidentally
Microscopic Pathology
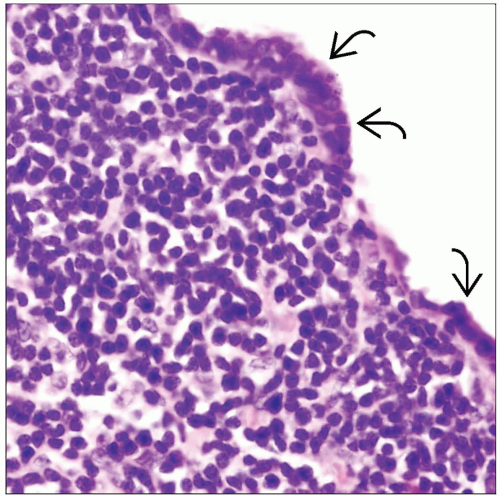
Nodular lymphoid hyperplasia (nodular BALT hyperplasia)
Multiple coalescent enlarged follicles showing prominent germinal centers
Interfollicular lymphoplasmacytosis
Follicular bronchiolitis
Discrete accumulations of small lymphoid aggregates in peribronchiolar location
Sparing of alveolar septa by lymphoid infiltrates
Diffuse lymphoid (BALT) hyperplasia (diffuse interstitial pneumonia)
Predominantly interstitial proliferation of small lymphocytes distending alveolar septa
Process is generally bilateral and diffuse
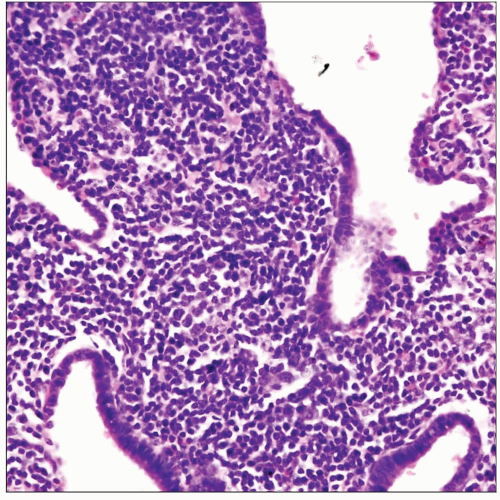 Diffuse BALT hyperplasia of the lung shows massively distended alveolar septa occupied by a population of small lymphoid cells. |
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Pseudolymphoma, nodular lymphoid hyperplasia, lymphoid interstitial pneumonia
Definitions
Polyclonal proliferation of small lymphocytes arising within lung parenchyma
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Pathogenesis
Commonly associated with underlying autoimmune disorders such as Sjögren syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, and collagen vascular diseases
Associated with viral infection, including HIV and Epstein-Barr virus
Associated with immunodeficiency, including common variable immunodeficiency, AIDS, and bone marrow transplants
Idiopathic
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Age
Adults 40-70 years of age (average = 50)
Diffuse form of the disease is more common in children
Gender
Female predilection
Presentation
Cough
Dyspnea
Asymptomatic; discovered incidentally
Dysproteinemia (hypergammaglobulinemia in 90% of patients)
May be associated with generalized lymphadenopathy or hepatosplenomegaly
Treatment
Surgical excision for localized lesions
Steroid therapy for diffuse lesions
Prognosis
Variable course depending on extent and progression of disease
Complete resolution is most common outcome
Diffuse cases may progress to end-stage pulmonary fibrosis with “honeycombing” of lung parenchyma
Diffuse cases may progress to diffuse lymphocytic lymphoma (MALT-lymphoma)
Death may ensue due to comorbid conditions, superinfection, or renal failure
IMAGE FINDINGS
General Features
Best diagnostic clue
Thin-walled cysts and centrilobular nodules
Location
Basilar interstitial thickening in adults with Sjögren syndrome
Radiographic Findings
Diffuse interstitial thickening, predominantly basilar
Multiple nodular pulmonary opacities, often with air bronchograms (more common in AIDS patients)
CT Findings
High-resolution CT scan shows nonspecific ground-glass opacities or consolidation
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree