Pulmonary Artery Sarcoma
Key Facts
Terminology
Synonym: Intimal sarcoma
Malignant mesenchymal tumor originating from wall of pulmonary trunk
Clinical Issues
Cough
Chest pain
Shortness of breath
Fatigue
Syncope
Macroscopic Features
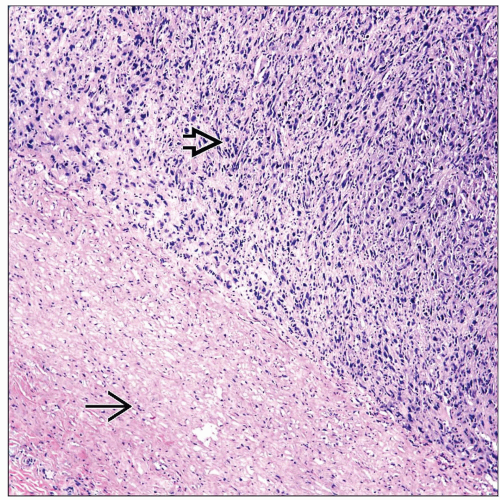
Most important characteristic is that tumor must be attached to pulmonary artery
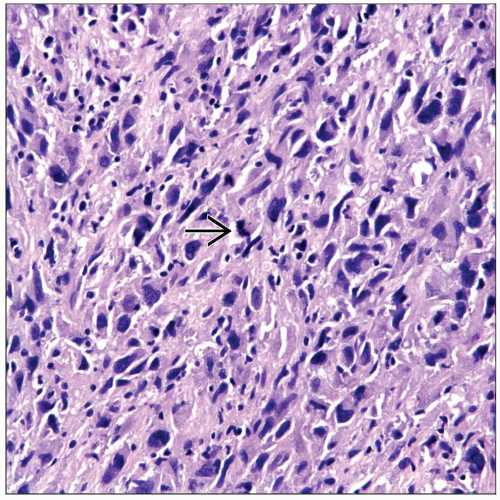
Microscopic Pathology
Varied mesenchymal differentiation
Angiosarcoma
Rhabdomyosarcoma
Chondrosarcoma
Osteosarcoma
Leiomyosarcoma
Top Differential Diagnoses
Metastatic sarcoma
Clinical history of extrathoracic tumor should lead toward correct interpretation
Primary intrapulmonary sarcoma
Identification of tumor into lumen of pulmonary artery is hallmark of this tumor
Diagnostic Checklist
Gross appearance
Wide spectrum of sarcomatous differentiation
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Pulmonary artery sarcoma (PAS)
Synonyms
Intimal sarcoma
Definitions
Malignant mesenchymal tumor originating from wall of pulmonary trunk
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Etiology
Has been suggested to arises from pluripotential cells
Most probably arises from pulmonary trunk
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Rare tumors that represent < 1% of all malignant mesenchymal tumors of lung
Age
Usually occurs in adults
Gender
No gender predilection has been observed in these tumors
Presentation
Cough
Chest pain
Shortness of breath
Fatigue
Syncope
Often confused for other medical conditions, such as pulmonary hypertension, pneumonia, or asthma
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Lobectomy or pneumonectomy
Adjuvant therapy
Chemotherapy &/or radiation may be of use depending on type of sarcoma
Prognosis
Intrathoracic metastasis may occur in 50% of patients
Extrathoracic metastasis may occur in about 15% of patients
Death may occur in a period of 12 months after initial diagnosis
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Tumor obliterating lumen of artery
Identification of pulmonary trunk
Identification of pulmonary artery
Polypoid tumor in intraluminal location
Sections to Be Submitted
Tangential sections to properly evaluate arterial wall