Pulmonary Amyloidosis
Key Facts
Terminology
Nonneoplastic process characterized by deposition of amorphous proteinaceous material that may involve lung either primarily or secondarily
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Secondary to
Systemic amyloidosis
Light chain disease
Multiple myeloma
MALT lymphoma of lung
Sjögren syndrome
Familial neuropathy
Gaucher disease
Microscopic Pathology
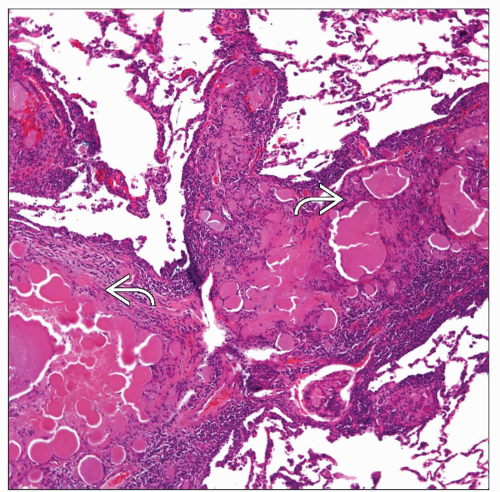
Several distinct patterns of amyloid deposition
Nodular
Interstitial
Diffuse
Plaque-like
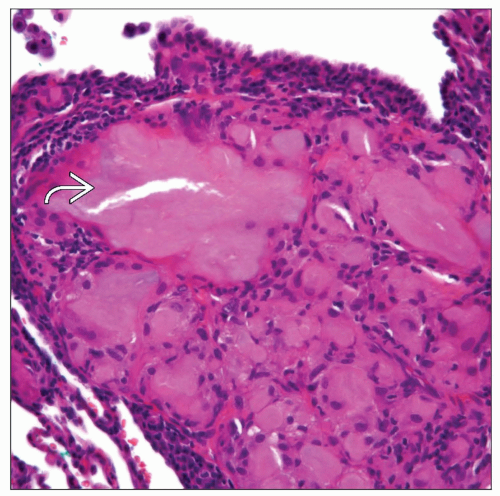
Cytologic features
Amorphous acellular material
Presence of giant cells toward periphery of lesion
Ossification may be present
Inflammatory reaction
Top Differential Diagnoses
Hyalinizing granuloma of lung
Alveolar proteinosis
Intrapulmonary solitary fibrous tumor (I-SFT)
Pneumocystis pneumonia
Pneumonia
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Amyloidoma
Definitions
Nonneoplastic process characterized by deposition of amorphous proteinaceous material that may involve lung either primarily or secondarily
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
May Develop Secondary to
Systemic amyloidosis
Light chain disease
Multiple myeloma
Waldenström macroglobulinemia
Familial neuropathy
Niemann-Pick disease
Gaucher disease
Sjögren syndrome
MALT lymphoma of lung
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Rare condition in lung
Age
Generally affects adults
Gender
No apparent gender predilection
Ethnicity
No apparent ethnic predilection
Site
Lung
Presentation
Dyspnea
Cough
Chest pain
Asymptomatic
Laboratory Tests
Potassium permanganate oxidation technique
Separates amyloid type AA from other forms of amyloid
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Surgical resection of tumor nodules is usually performed
Prognosis
Depends on clinical background, such as whether patient has systemic amyloidosis or any other disease associated with amyloid deposition
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Lung parenchyma can have 1 or more pulmonary nodules
Size
Varies; between 1 and > 10 cm
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Several distinct patterns of amyloid deposition in lung
Nodular
Interstitial
Diffuse
Plaque-like
Cytologic Features
Amorphous acellular material
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree