Class
- Antipsychotic, antiemetic
Prochlorperazine
Commonly Prescribed for
(FDA approved in bold)
- Schizophrenia
- Nonpsychotic anxiety in adults
- Severe nausea and vomiting
- Migraine
- Vertigo and labyrinthine disorders
- Mania in bipolar disorder
Prochlorperazine
 How the Drug Works
How the Drug Works
- Dopamine receptor antagonist with greater action at D2 receptors. Also blocks serotonin 2A receptors, alpha-adrenergic receptors and is an antihistamine
Prochlorperazine
How Long Until It Works
- Injection effective within 10 minutes, oral 1–2 hours
Prochlorperazine
If It Works
- Use at lowest effective dose
- Monitor QT corrected (QTc) interval
- Continue to assess effect of the medication and if it is still needed
Prochlorperazine
If It Doesn’t Work
- Increase dose, or discontinue and change to another agent
Prochlorperazine
 Best Augmenting Combos for Partial Response or Treatment-Resistance
Best Augmenting Combos for Partial Response or Treatment-Resistance
- Migraine: often combined with NSAIDs and triptans or ergots
- Nausea and vomiting: corticosteroids
Prochlorperazine
Tests
- Monitor weight, blood pressure, lipids, and fasting glucose with frequent chronic use. Obtain blood pressure and pulse before initial IV use and monitor QTc with ECG
Adverse Effects (AEs)
Prochlorperazine
How Drug Causes AEs
- Motor AEs and prolactinemia – blocking of D2 receptors
- Hypotension – blocking of alpha-1 adrenergic receptors
Prochlorperazine
Common AEs
- Most common: Dizziness, sedation, dry mouth, constipation, skin changes
- Tachycardia, hypo- or hypertension
- Akathisia, parkinsonism
Prochlorperazine
 Life-Threatening or Dangerous AEs
Life-Threatening or Dangerous AEs
- Tardive dyskinesias
- ECG changes including prolongation of QTc. Rarely cardiac arrest
Prochlorperazine
Weight Gain
- Common
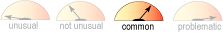
- With frequent use
Prochlorperazine
Sedation
- Common
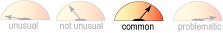
Prochlorperazine
What to Do About AEs
- Rarely causes ECG changes. Use with caution if QTc is above 450 (women) or 440 (men) and do not administer with QTc greater than 500
- If excessive sedation occurs, use only as a rescue agent for inpatients or when patients can lie down or sleep
Prochlorperazine
Best Augmenting Agents for AEs
- Give fluids to avoid hypotension, tachycardia, and dizziness
- Give anticholinergics (diphenhydramine or benztropine) or benzodiazepines for extrapyramidal reactions
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


