Chapter 27 Problems with lipid metabolism
Fatty acids are an important source of energy: potentially, triglycerides can release as much energy per kilogram as carbohydrates or proteins. Lipids are components of membranes in the form of phospholipids (see Chapter 10 ‘Lipids’, p. 73).
Fatty acids are usually eaten as triglycerides, which are broken down into free fatty acids and monoglycerides by lipases in the small intestine. This process is assisted by bile salts, which emulsify the fats and increase the efficiency of the enzymes (see Chapter 4 ‘Bonds continued’, p. 25).
There are four main classes of lipoprotein:
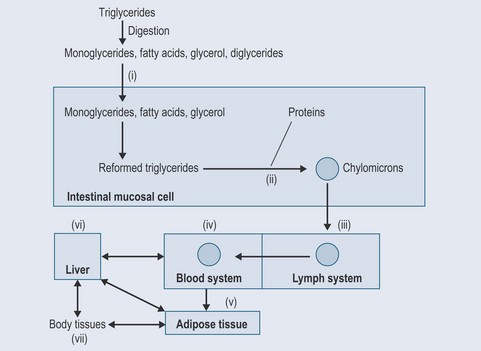
What Happens to Lipids after Absorption?
Figure 27.1 outlines the fate of lipids after absorption. The numbers below correspond to those in the illustration:
If the lipids are unused, they are stored.
Atherosclerosis
Thrombus Formation
Figure 27.2 illustrates the formation of a thrombus, which is the basis of atherosclerosis. The numbers below relate to those in the illustration:
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree