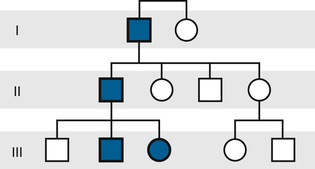
8. Given the pedigree below, what is/are the most likely inheritance pattern(s); possible but less likely inheritance pattern(s); incompatible inheritance pattern(s)? Patterns are autosomal recessive, autosomal dominant, X-linked recessive, X-linked dominant, mitochondrial. Justify your choices.
9. When a child is affected with an autosomal recessive condition, the assumption is that both parents are heterozygous carriers for the condition. Yet, new mutations occur all the time during the generation of gametes (see Chapter 4). Might not an individual have two mutant alleles for an autosomal recessive condition by virtue of inheriting one mutant allele from a carrier parent, whereas the other mutant allele arose de novo in a gamete that came from a parent who was not a carrier? Consider a child with cystic fibrosis. Calculate the odds (ratio of the probabilities) that both parents are carriers versus the probability that only the mother is a carrier and the sperm brought in a de novo mutation. Assume an average mutation rate of approximately 1 ×10−6 per male gamete per generation.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


