Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor
Satish K. Tickoo, MD
Victor E. Reuter, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Primitive neuroectodermal tumor (PNET)
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Nontype 1 gene fusions in ES/PNET of soft tissue are associated with poor outcome
Ewing sarcoma (ES)/PNET family of tumors characterized by fusion of EWS with gene from ETS (E-twenty six) family of transcription factors
Clinical Issues
Most common in young adults and adolescents
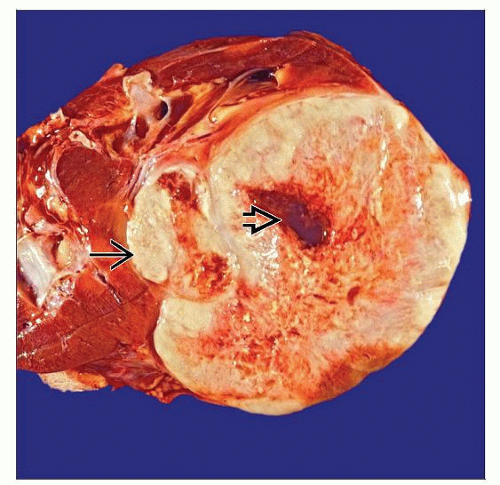
Macroscopic Features
Usually large, with mean diameter 16 cm (range: 7-21 cm)
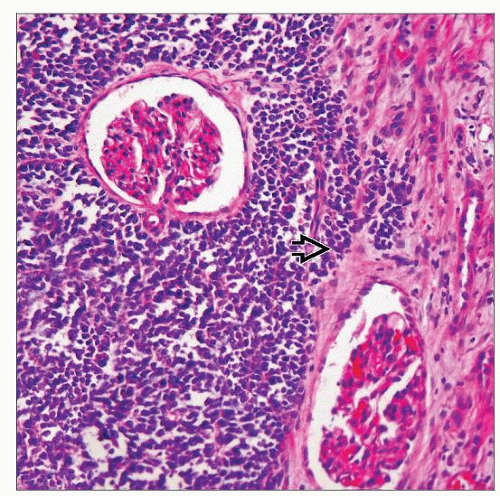
Microscopic Pathology
Identical to their soft tissue counterparts
Vaguely lobulated proliferations of primitive-appearing round cells with high nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio
Occasionally with small amount of clear cytoplasm, and more vesicular nuclei showing small nucleoli
Epithelial, myogenous, or cartilaginous differentiation not seen
ES/PNET strongly and diffusely positive in membranous pattern for CD99; most, but not all, with FLI-1 nuclear positivity
Top Differential Diagnoses
Blastemal Wilms tumor
Other small blue round cell tumors
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Primitive neuroectodermal tumor (PNET)
Definitions
Aggressive small blue round cell tumor characterized by fusion of EWS gene with a gene from ETS (E-twenty six) family of transcription factors
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Molecular Features
Similar to Ewing sarcoma (ES)/PNET of bone and soft tissue
Primary renal PNET also demonstrates characteristic EWS-FLI1 gene fusion resulting from translocation t(11;22)(q24;q12)
In bone and soft tissue, 70% of EWS/FLI1 gene fusions involve fusion of EWS exon 7 and FLI1 exon 6 (so-called type 1 fusion)
Nontype 1 gene fusions in ES/PNET of soft tissue are associated with poor outcome
In renal PNET, only 1/2 have demonstrated type 1 fusion, while other 1/2 have variant fusions
Other than FLI1, genes of ETS family that may be fused with EWS include, ERG, ETV1, E1AF, FEV, ZSG
Increased predilection for variant gene fusions in renal cases may contribute to their more adverse prognosis
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Very uncommon; approximately 120 cases described in literature
Age
Most common in young adults and adolescents; mean age: 27 years (range: 10-60 years)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree