Primary Cutaneous Follicle Center Lymphoma
Aaron Auerbach, MD, PhD
Key Facts
Terminology
PCFCL
Mature B-cell lymphoma of follicle center cells, primary to skin and not originating in another anatomic site
Clinical Issues
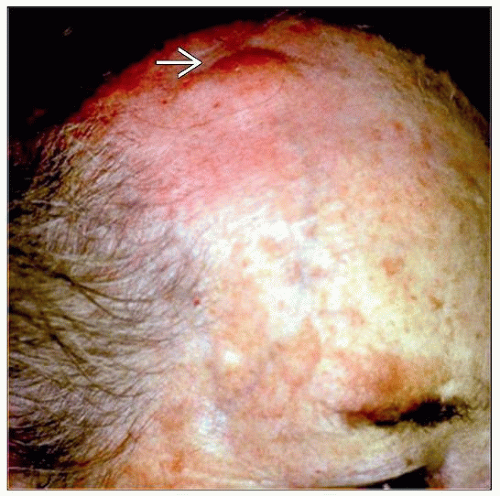
Mostly single lesion on scalp; trunk 2nd most common site
> 95% 5-year survival with local recurrences
Microscopic Pathology
Nodular, diffuse, and nodular/diffuse growth patterns
Lack of mantle zones, lack tingible body macrophages
Ancillary Tests
CD20(+), Bcl-6(+), CD10(+/−) (often negative in diffuse variant)
Bcl-2(−/+) and MUM1(−)
CD23, CD21, and CD35 positive in FDC meshworks
Usually CD43(−), unlike other B-cell lymphomas
CD5(−), Bcl-1(−)
Clonal Ig heavy chain (IgH) gene rearrangement
t(14;18), often not detected
Gene expression profiling findings akin to germinal center-like large B-cell lymphoma
Top Differential Diagnoses
Reactive follicular hyperplasia
Primary cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma
Secondary skin involvement of follicular lymphoma
Primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type
Primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, NOS
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Primary cutaneous follicle center lymphoma (PCFCL)
Synonyms
Follicular lymphoma of skin
Crosti disease (reticulohistiocytoma of dorsum)
Plaques/tumors surrounded by erythematous macules/papules
Definitions
Mature B-cell lymphoma of follicle center cells, primary in skin
Disease limited to skin for 6 months after diagnosis
Distinct disease from systemic follicular lymphoma
Better prognosis
Fewer BCL2 rearrangements than systemic follicular lymphoma
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
0.1-0.2 cases per 100,000 people per year
Most common primary cutaneous B-cell lymphoma
˜ 20% of all skin lymphomas
˜ 60% of all B-cell skin lymphomas
Age
Usually adults
Median age: 60 years
But can also be seen in childhood
Gender
Male:female = 1.5:1
Site
Usually head and neck, especially scalp
Less commonly trunk
Presentation
Usually single lesion
˜ 15% multifocal
Plaques, nodules, or tumors of differing sizes
From < 1 cm to > 40 cm in greatest dimension
Rarely ulcerates
Treatment
Observation, surgical removal or local radiation
Chemotherapy only if extensive disease or extracutaneous disease
Prognosis
Good
Much better than systemic follicular lymphoma
Usually complete remission with treatment
˜ 95% 5-year survival
Not affected by
Grade or growth pattern
Bcl-2 expression or t(14;18) status
˜ 35% recurrence (often proximal to original lesion); extracutaneous spread ˜ 10%
˜ 10% disseminate to extracutaneous sites
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
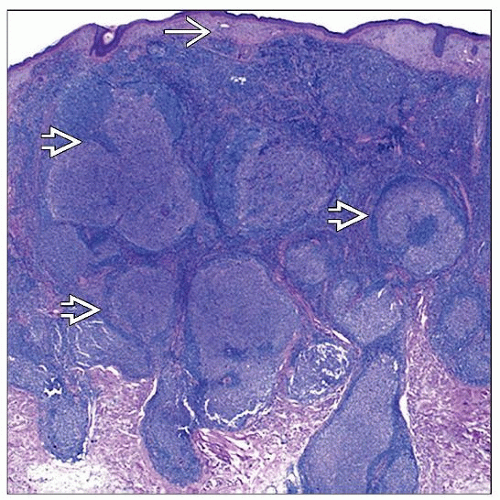
Dermal B-cell infiltrate, often extends into subcutis (˜ 75%)
No overlying epidermotropism
Growth pattern
Nodular, diffuse, or nodular and diffuse
May be classified as follicular (> 75% follicular architecture), follicular and diffuse (25-75% follicular architecture), or diffuse (< 25% follicular architecture) growth pattern
Follicles
Often not well-defined
Usually seen in small lesions
Lack mantle zones
Lack tingible body macrophages
Contain follicular dendritic cells
Tumor cells
Mostly centrocytes (small to medium-sized, cleaved)
Variable numbers of centroblasts (larger in size)
Cases with ↑ numbers of centroblasts
Diagnose as PCFCL if nodular or nodular and diffuse growth pattern
Diagnose as diffuse pattern PCFCL if large cells and only diffuse growth pattern
Grading of follicular lymphoma
Not necessary or of prognostic value for PCFCL
Is necessary for systemic follicular lymphoma
Grade 1: < 5 centroblasts per high-power field; grade 2: 6-15 centroblasts per high-power field; grade 3: > 15 centroblasts per high-power field
Grades 1 and 2 show minimal differences in long-term outcome
Thus, 2008 WHO classification lumps cases with few centroblasts as “follicular lymphoma grade 1-2 (low grade)” in systemic follicular lymphoma, and does not advise grading of PCFCL
Cytologic Features
Small cleaved cells with coarse chromatin and 1 or more indistinct nucleoli on peripheral smear
ANCILLARY TESTS
Immunohistochemistry
B-cell markers positive
CD20, CD19, CD79a, pax-5
Mostly MUM1 negative, unlike primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type
Follicle center markers positive
Bcl-6(+); CD10(+/−) (usually negative in diffuse areas)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree