Pouchitis
Joel K. Greenson, MD
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
Acute pouchitis may be due to bacterial overgrowth and respond to antibiotics
Chronic relapsing pouchitis that does not respond to antibiotics may require steroids or immunomodulator therapy
If refractory to drug therapies, surgical removal of pouch with ileostomy is alternative
Microscopic Pathology
Hallmark of pouchitis: Active inflammation on top of chronic changes
Top Differential Diagnoses
Normal pouch histology
Crohn disease
Cuffitis
Recurrent in UC in rectal cuff
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
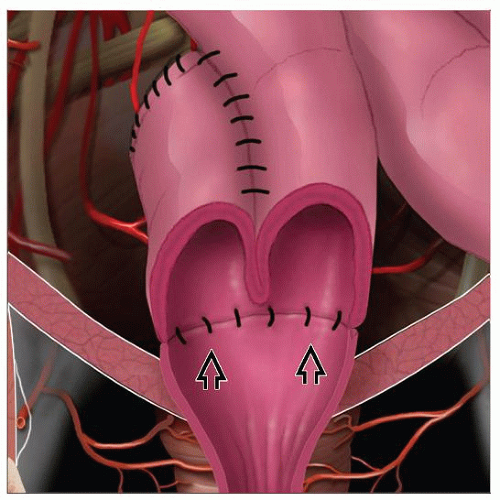
Nonspecific inflammatory condition affecting ileal reservoir after ileal pouch anal anastomosis (IPAA)
Chronic relapsing condition
Much more common in ulcerative colitis (UC) patients than familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) patients
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Acute Pouchitis
Typically results from bacterial overgrowth
Some patients require chronic antibiotic therapy
Chronic Relapsing Pouchitis
Much more common in UC patients, especially those with primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC)
Probably UC affecting pouch
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree