Poroma and Dermal Duct Tumor
David Cassarino, MD, PhD
Key Facts
Terminology
Eccrine poroma
Apocrine poroma
Hidroacanthoma simplex (intraepidermal poroma, syringoacanthoma)
Acrospiroma (older term, includes poroma and hidradenoma)
Benign adnexal proliferation with anastomosing cords of cells and ductal differentiation
Clinical Issues
Relatively common tumors
Usually occur in middle-aged adults
Most common on the extremities, especially the palmar and plantar surfaces
Solitary pink to reddish papular or nodular lesion
Excellent prognosis in most cases
Microscopic Pathology
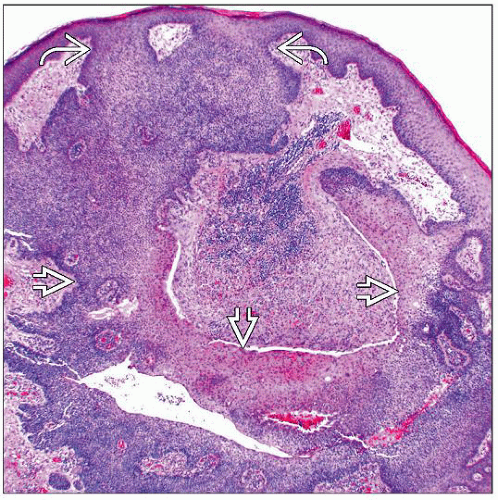
Symmetric, well-circumscribed tumor with multiple epidermal attachments (except in dermal duct tumor)
Broad, anastomosing columns and thickened cords of tumor cells
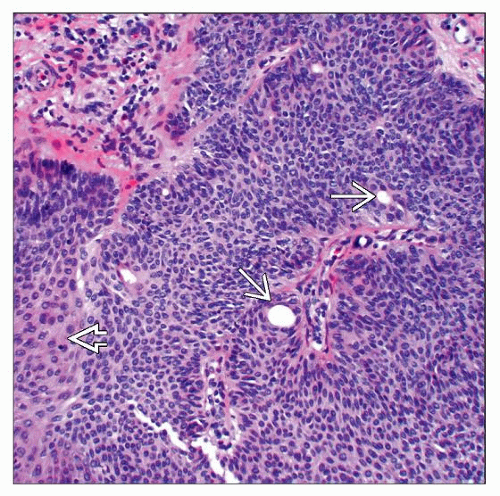
Ductal lumina typically well-formed, numerous
Cells may be basaloid, squamoid, clear, or pigmented
Mitotic figures may be present, and can be numerous in traumatized lesions
Top Differential Diagnoses
Hidradenoma
Irritated/clonal seborrheic keratosis (SK)
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC)
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)
Porocarcinoma (malignant poroma)
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Apocrine poroma
Eccrine poroma
Hidroacanthoma simplex (intraepidermal poroma, syringoacanthoma)
Acrospiroma (older term, includes both poroma and hidradenoma)
Definitions
Benign adnexal proliferation with anastomosing cords of tumor cells exhibiting ductal differentiation
Typically has multiple epidermal attachments, except for dermal duct tumor
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Unknown
Rare cases associated with radiation therapy and pregnancy
May rarely be multiple (“poromatosis”)
Formerly considered eccrine, but many cases likely of apocrine differentiation
May see sebaceous &/or follicular differentiation in apocrine cases
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Relatively common tumors
Age
Usually occur in middle-aged adults
Gender
Equal incidence in males and females
Site
Most common on the extremities, especially the palmar and plantar surfaces
May also occur on the trunk, head and neck
Presentation
Solitary pink to reddish papular or nodular lesion
Some cases may be very vascular and bleed easily
Minority of cases are pigmented
Natural History
Stable lesions; do not usually regress
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Complete conservative excision is curative
Typically recommended to prevent recurrence and rare transformation to porocarcinoma
Prognosis
Excellent; most cases do not show aggressive behavior
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Superficial, firm papule or nodule
Size
Generally < 1 cm but may be larger
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Symmetric, well-circumscribed tumor with multiple epidermal attachments
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree