Pleomorphic Liposarcoma
Thomas Mentzel, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Pleomorphic high-grade sarcoma containing variable amounts of pleomorphic lipoblasts
Clinical Issues
Rarest subtype of liposarcoma
Accounts for approximately 5% of all liposarcomas
Most cases arise in elderly patients (> 50 years old)
Most cases arise on extremities (lower > upper)
Most cases arise in deep soft tissues
Clinically aggressive neoplasm
30-50% metastasis rate
5-year survival rate of 60-65%
Deep-seated large neoplasms are associated with worse prognosis
> 20 mitoses per 10 high-power fields and necrosis are associated with worse prognosis
Surgical approach: Complete wide excision with tumor-free margins
High-grade sarcoma
Microscopic Pathology
Well-circumscribed, nonencapsulated, or ill-defined infiltrative neoplasms
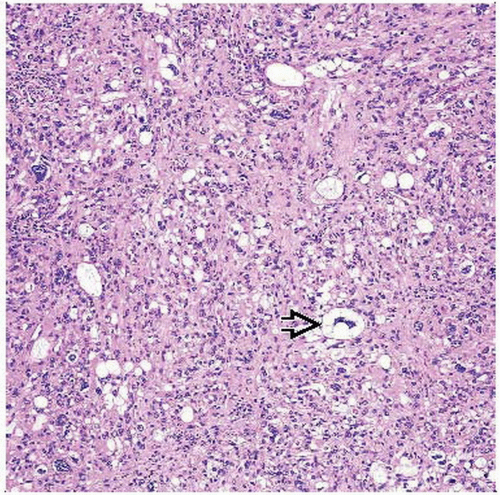
High-grade sarcoma associated with variable amounts of pleomorphic lipoblasts
Sheets or single pleomorphic lipoblasts
Pleomorphic lipoblasts contain enlarged, hyperchromatic nuclei scalloped by cytoplasmic vacuoles
Intermediate- or high-grade myxofibrosarcoma-like areas may be present
Epithelioid pleomorphic liposarcoma variant
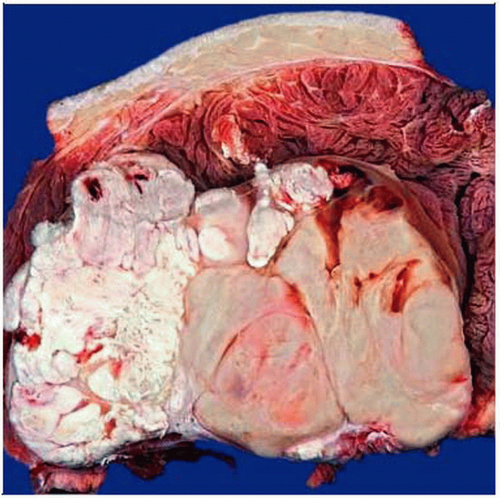 Gross photograph shows an intramuscular, partly necrotic neoplasm with gray-white indurated cut surfaces. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Pleomorphic liposarcoma (PLS)
Definitions
Pleomorphic high-grade sarcoma containing variable amounts of pleomorphic lipoblasts
No areas of atypical lipomatous tumor are present
No sarcomatous component of a different line of differentiation is present
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Rarest subtype of liposarcoma
Accounts for approximately 5% of all liposarcomas
Accounts for approximately 20% of all pleomorphic sarcomas
Age
Most cases arise in elderly patients (> 50 years old)
Gender
Equal sex distribution
Site
Most cases arise in extremities (lower > upper)
Trunk and retroperitoneum are more rarely involved
Rare sites include mediastinum, paratesticular region, scalp, abdominal/pelvic cavities
Most cases arise in deep soft tissues
Subcutaneous cases are rare
Purely dermal cases are very rare but may occur
Presentation
Deep mass
Painless mass
Firm enlarging mass
Natural History
Many patients have short preoperative history
Clinically aggressive neoplasm
30-50% metastasis rate
Lung represents preferred site of metastases
40-50% overall tumor-associated mortality
5-year survival rate of 60-65%
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Complete wide excision with tumor-free margins
Adjuvant therapy
Postoperative radiotherapy may be given for large, incompletely excised neoplasms
Prognosis
High-grade sarcoma
Worse prognosis than dedifferentiated liposarcoma
Better prognosis than high-grade myogenic sarcomas
Deep-seated large neoplasms are associated with worse prognosis
> 20 mitoses per 10 high-power fields and necrosis are associated with worse prognosis
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Firm, often multinodular neoplasms
White to yellow cut surfaces
May show myxoid areas
May show areas of tumor necrosis
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Well-circumscribed, nonencapsulated, or ill-defined infiltrative neoplasms
High-grade sarcoma associated with variable number of pleomorphic lipoblasts
Sheets or single pleomorphic lipoblasts
Pleomorphic lipoblasts contain enlarged, hyperchromatic nuclei scalloped by cytoplasmic vacuoles
Sarcomatous component contains atypical spindled, round, and pleomorphic tumor cells
Numerous mono- and multinucleated tumor giant cells
High degree of nuclear atypia
Numerous mitoses
Areas of tumor necrosis are often present
Intermediate- or high-grade myxofibrosarcoma-like areas may be present
Intra- and extracellular eosinophilic droplets (represent lysosomal structures) are noted
Rarely prominent inflammatory infiltrate is evident
Epithelioid pleomorphic liposarcoma variant
Contains solid, cohesive sheets of epithelioid tumor cells
Foci of atypical lipogenic cells
Variable number of pleomorphic lipoblasts
Small round cell variant
Small round tumor cells
Variable number of pleomorphic lipoblasts
Predominant Pattern/Injury Type
Hypercellular
Predominant Cell/Compartment Type
Lipoblast
Undifferentiated, pleomorphic