Pleomorphic Carcinoma
Key Facts
Terminology
Malignant epithelial neoplasm composed of spindle and multinucleated giant cells in different proportions
Etiology/Pathogenesis
PC may represent a genetically distinct type of malignancy separate from squamous and adenocarcinoma
Clinical Issues
Symptoms
Chest pain
Hemoptysis
Cough
Prognosis
Majority of cases are in advanced clinical stages
Prognosis is poor
Lobectomy or pneumonectomy
Chemotherapy or radiation therapy depending on clinical setting
Microscopic Pathology
Mixture of 2 distinct components, sarcomatoid and giant cells
Top Differential Diagnoses
Malignant fibrous histiocytoma (MFH)
Pulmonary leiomyosarcoma
Sarcomatoid carcinoma
Metastatic choriocarcinoma
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Pleomorphic carcinoma (PC)
Synonyms
Giant cell carcinoma, carcinoma with giant cells, carcinoma with pseudosarcomatous stroma, pseudosarcomatous carcinoma, metaplastic carcinoma
Definitions
Malignant epithelial neoplasm composed of spindle and multinucleated giant cells in different proportions
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Etiology
PC may represent a genetically distinct type of malignancy separate from squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
Asymptomatic
Chest pain
Hemoptysis
Cough
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Lobectomy or pneumonectomy
Adjuvant therapy
Chemotherapy or radiation therapy depending on clinical setting
Prognosis
Depends on stage at diagnosis
Majority of cases are in advanced clinical stages
Prognosis is poor
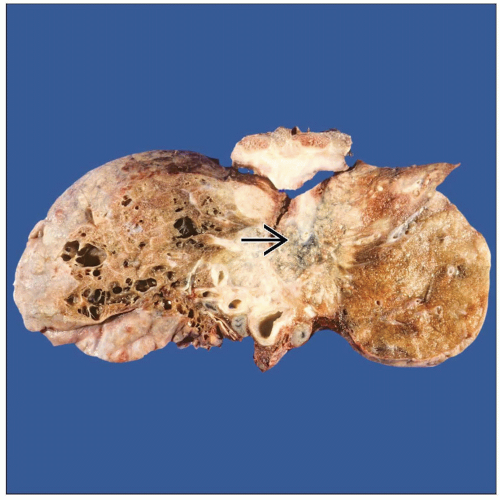
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Central or peripheral
Varying size but generally large tumors
Well circumscribed but not encapsulated
Light tan with homogeneous cut surface
Areas of necrosis &/or hemorrhage may be seen
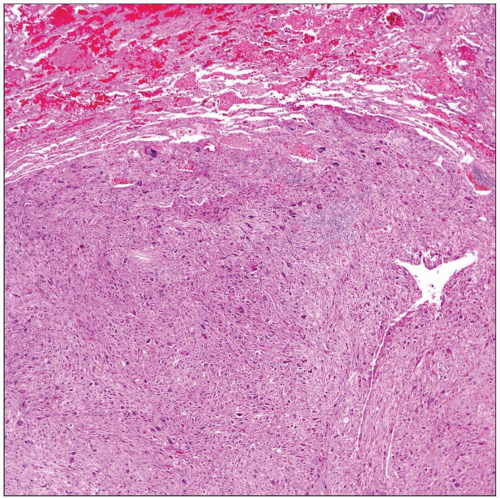
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Mixture of 2 distinct components, spindle and giant cells
Predominant Pattern/Injury Type
Sarcomatoid
Predominant Cell/Compartment Type
Epithelial
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Malignant Fibrous Histiocytoma (MFH)
Touton-type giant cells in MFH; multinucleated malignant cells in PC
Areas of squamous cell carcinoma or adenocarcinoma in most cases of PC
Studies using keratin antibodies helpful as sarcomatoid component may show keratin expression
MFH may also show focal positive staining for keratin
Pulmonary Leiomyosarcoma
Immunohistochemistry studies for desmin, caldesmon, and SMA generally negative in PC cases while positive in leiomyosarcomas
Presence of multinucleated giant cell component is not a common feature, even in cases of high-grade leiomyosarcoma
Most pulmonary leiomyosarcomas are confined to lung, while PC is commonly in advanced clinical stage
Sarcomatoid Carcinoma
Though sarcomatoid carcinoma and PC are often coded under same category, PC has sarcomatoid component in association with multinucleated giant cells
Sarcomatoid carcinoma shows only spindle cell component
Both tumors share similar immunohistochemical profile
Metastatic Choriocarcinoma
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree