Placental Transmogrification
Key Facts
Terminology
Synonyms: Placentoid bullous lesion, giant bullous emphysema, pulmonary lipomatosis
Benign unusual condition characterized by bizarre changes in shape of normal lung parenchyma
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Some cases have been associated with tobacco use, others with a pneumonic process
Clinical Issues
Process can be seen in adult or young adults
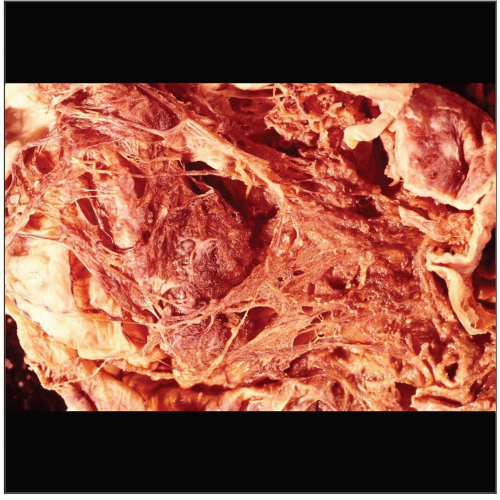
Macroscopic Features
Ill-defined process with complete degeneration of normal lung parenchyma
Cystic changes
Grape-like structures
Soft consistency and yellowish color
Ill-defined; may involve entire lobe or lobe segment
Top Differential Diagnoses
Pneumonia
Shows areas of acute and chronic inflammatory cells, which are commonly absent in transmogrification
Emphysema
There is very little residual alveoli in transmogrification
Extensive areas of papillary-like structures with adipose tissue
Papillary carcinoma
Most likely would present as pulmonary mass
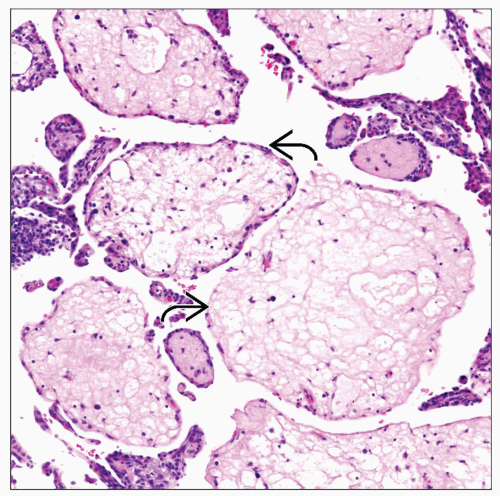
 This portion of lung shows placental transmogrification. Note the grotesque appearance of the lung parenchyma. |
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Placentoid bullous lesion, giant bullous emphysema, pulmonary lipomatosis
Definitions
Benign unusual condition characterized by bizarre changes in shape of normal lung parenchyma
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Environmental Exposure
Some cases have been associated with tobacco use
Infectious Agents
Some cases have been associated with pneumonic process
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
This process can be seen in the elderly or young adults
Presentation
Cough
Fever
Pneumonia
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Complete surgical resection
Prognosis
Good
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Ill-defined process with complete degeneration of normal lung parenchyma
Cystic changes
Grape-like structures
Soft consistency and yellowish color
Size
Ill-defined; may involve entire lobe or lobe segment
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Papillary features without cellular atypia or mitotic activity
Papillary component may show
Myxoid changes
Lipomatous changes
Edematous changes
Minimal inflammatory changes
Placental-like pattern
In focal areas, residual alveolated tissue may be present
In focal areas, residual airway may be seen
Lack of pulmonary fibrosis
Focal calcifications may be seen
Predominant Pattern/Injury Type
Ill-defined
Predominant Cell/Compartment Type
Foamy
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Pneumonia
Emphysema
Presence of papillary structures with myxoid or lipomatous changes would be unusual for emphysema
Entire lung parenchyma is destroyed in transmogrification
Leaves little residual alveoli
Papillary Carcinoma
Lack of nuclear atypia or mitosis is feature of placental transmogrification
Presence of myxoid or lipomatous changes would be unusual for carcinoma
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree