Paraffinoma (Lipoid Pneumonia)
Key Facts
Terminology
Synonyms
Cholesterol pneumonia, lipoid pneumonia, golden pneumonia
Definition: Type of pneumonia that could be secondary to aspiration; can be classified as
Endogenous
Exogenous
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Exogenous
Aspiration of oily substances
Mineral oil
Vegetable oil
Petroleum jelly
Oil mists
Some radiographic contrast media
Endogenous
Result of pulmonary obstruction or gastroesophageal reflux
May result as a breakdown of cell membrane or lipoprotein secretions
Clinical Issues
Rare; may be seen in bedridden patients
Can occur in any age group, children or elderly
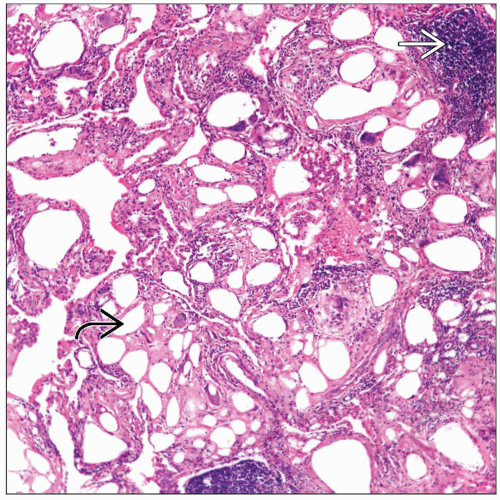
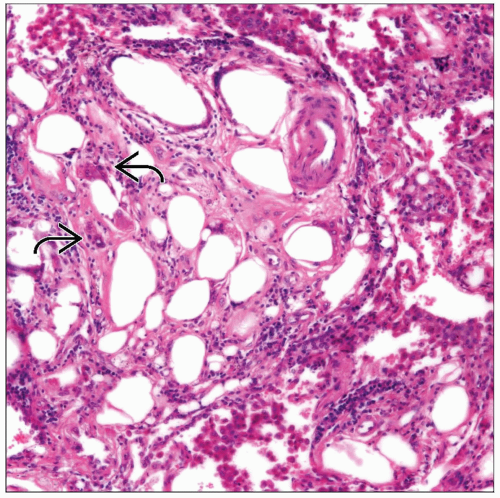
Microscopic Pathology
Proliferation of foamy histiocytes
Cholesterol cleft granulomas
Foreign body giant cell reaction
Fat droplets in interstitium
Inflammatory reaction may be minimal
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Cholesterol pneumonia, lipoid pneumonia, golden pneumonia, exogenous/endogenous lipoid pneumonia
Definitions
Type of pneumonia secondary to aspiration; can be classified as
Endogenous
Exogenous
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Etiology
Exogenous
Aspiration of oily substances
Mineral oil
Vegetable oil
Petroleum jelly
Oil mists
Some radiographic contrast media
Endogenous
Result of pulmonary obstruction or gastroesophageal reflux
May result from breakdown of cell membrane or lipoprotein secretions
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Rare; may be seen in bedridden patients
Age
Can occur in any age group, children or elderly
Gender
No gender predilection
Presentation
Cough
Chest pain
Dyspnea
Fever
Treatment
In cases of endogenous lipoid pneumonia, dealing with cause of obstruction may be beneficial
In cases of exogenous lipoid pneumonia, identification and stopping of probable cause is crucial
Antibiotics may be necessary
Prognosis
Depends on origin, but in some cases, endogenous lipoid pneumonia can be fatal
IMAGE FINDINGS
Radiographic Findings
May be a mixture of interstitial and alveolar pattern
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Soft and yellowish consolidated areas
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Cytologic Features
Fat droplets in interstitium
Positive staining in frozen tissue for oil red O
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Mycobacterial Infection
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree