Paclitaxel (Taxol) Effect
Elizabeth A. Montgomery, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Pattern of mitotic arrest and apoptosis of the gastrointestinal tract mucosa associated with administration of paclitaxel (Taxol)
Clinical Issues
Excellent prognosis in most cases
Usually findings are incidental, rather than reflection of toxicity
Reports of colonic perforation and acute abdomen following taxane administration
Often found incidentally in mucosal biopsies obtained within 1-4 days of drug administration
Important to correlate with clinical findings
Can be found in association with paclitaxel toxicity
Microscopic Pathology
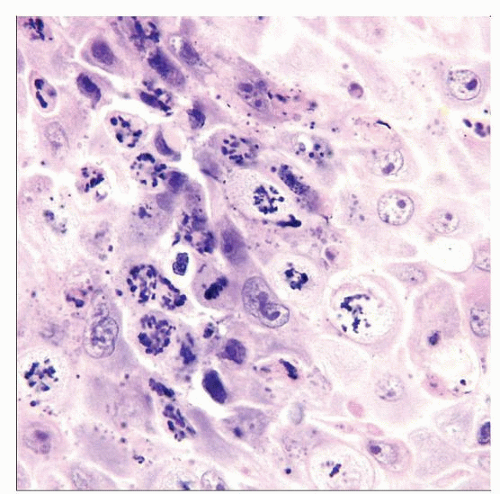
Prominent apoptosis and mitotic arrest
Ring mitoses
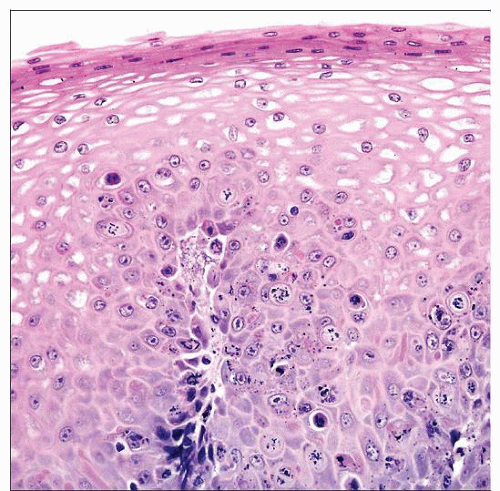 Hematoxylin & eosin shows paclitaxel effect in squamous mucosa. The proliferative compartment of squamous mucosa is at the base, so this is the site of mitotic arrest. |
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Taxane effect, paclitaxel effect
Definitions
Pattern of mitotic arrest and apoptosis of gastrointestinal tract mucosa associated with administration of paclitaxel (Taxol)
Other drug in class of taxanes is docetaxel (Taxotere)
Paclitaxel originally isolated from bark of Pacific yew tree, Taxus brevifolia
Paclitaxel works by interfering with normal microtubule breakdown during cell division
Also activates apoptosis by inducing Bcl-2 phosphorylation, which inhibits Bcl-2 binding to BAX, with subsequent increase in apoptosis
Important chemotherapeutic agents
Used to treat cancer of esophagus, breast, and lung, as well as advanced Kaposi sarcoma
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
Characteristic histologic changes can be found incidentally in mucosal biopsies or resections obtained within 1-4 days of administration of paclitaxel
Can also be found in association with paclitaxel toxicity
Reported symptoms and associations
Vomiting
Diarrhea
Mucositis
Neutropenic enterocolitis
Colonic perforation
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree