Overview of Myelodysplastic/Myeloproliferative Neoplasms
Kathryn Foucar, MD
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasms (MDS/MPN)
Definitions
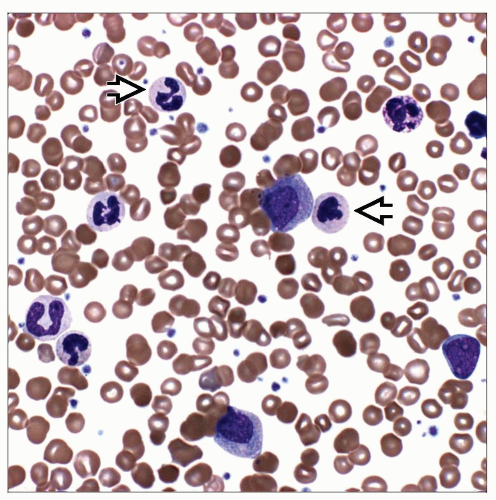
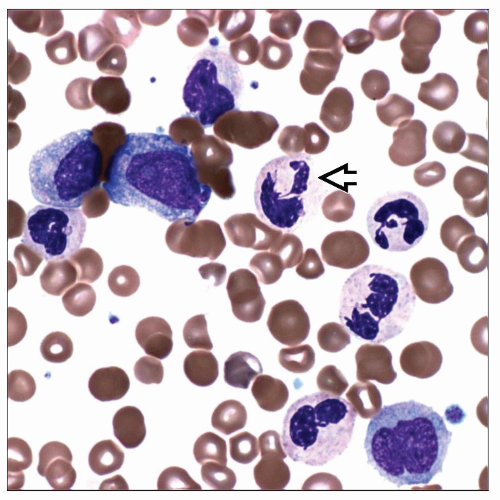
De novo clonal chronic myeloid neoplasm characterized by hybrid myelodysplastic and myeloproliferative features manifested by at least 1 cytopenia and at least 1 cytosis in blood
Maturation is intact, mature cells predominate
Blasts and blast equivalents are < 20% in blood and bone marrow
Multiple subtypes defined with specific criteria
WHO 2008 Classification of MDS/MPN
Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML)
Atypical chronic myeloid leukemia, BCR-ABL1 negative (aCML)
Juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia (JMML)
Myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasm, unclassifiable (MDS/MPN-U)
Refractory anemia with ring sideroblasts and thrombocytosis (RARS-T) (provisional category)
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Molecular Genetic Findings
No disease defining molecular/cytogenetic features
Aberrations in RAS/MAPK signaling pathways common and linked to abnormal cell proliferation
May include mutations in PTNPN11, NRAS, KRAS, or NF1 most notably in JMML
Many exclusionary genetic findings including absence of BCR-ABL1, PDGFRA/B, FGFR1 mutations, isolated del(5q), inv3(q21q26), and AML-defining translocations
All of these mutations are pathogenetically linked to other types of myeloid neoplasms
EPIDEMIOLOGY