Overview and Classification of Mature Leukemias, Immunosecretory Lymphomas
Kaaren K. Reichard, MD
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Clonal B-cell or plasma cell-derived neoplasms composed of morphologically &/or immunophenotypically mature B or plasma cells
Characteristic peripheral blood (PB) and bone marrow (BM) involvement in B leukemias and plasma cell neoplasms
Variable involvement of PB/BM with B-cell lymphomas
Classification of Mature B-cell Leukemias
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL)
B-cell prolymphocytic leukemia (B-PLL)
Hairy cell leukemia (HCL)
Splenic B-cell lymphoma/leukemia, unclassifiable
Classification of Mature B-cell Lymphomas That May Involve PB/BM
Splenic B-cell marginal zone lymphoma (SMZL)
Follicular lymphoma (FL)
Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL)
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL)
Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma
ALK(+) DLBCL
Plasmablastic lymphoma
Burkitt lymphoma
Classification of Plasma Cell Neoplasms
Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma (LPL)
Gamma heavy chain disease
Monoclonal gammopathy of uncertain significance (MGUS)
Plasma cell myeloma (PCM)
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Highly variable
CLL/SLL common
FL and DLBCL common
MGUS common
ALK(+) DLBCL rare
Age range
Highly variable
Plasma cell neoplasms typically affect adults
Burkitt lymphoma seen in children and adults
Other mature B cell leukemias and lymphomas tend to affect adults
Site
PB/BM
Typical of leukemias
Typical of plasma cell neoplasms
Extramedullary sites with possible involvement of PB/BM
B-cell lymphomas
Presentation and Natural History
CLL/SLL, SMZL, HCL generally indolent
B-PLL generally aggressive
DLBCL, Burkitt lymphoma, plasmablastic lymphoma; aggressive, yet potentially curable
Mantle cell lymphoma generally aggressive
Laboratory Tests
Complete blood cell count (CBC) with differential
PB smear review
BM biopsy
Flow cytometry
Genetics depending on disease type
Immunohistochemistry for ALK-, EBV-, and HHV8-related disease
Treatment
Highly variable
Depends on disease
Patients with indolent disease may not require therapy
Chemotherapy &/or other therapies for aggressive tumors
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Highly Variable
Subtype dependent
Translocations
FL and subset of DLBCL with t(14;18)(q32;q21); IGH@-BCL2 fusion
Burkitt lymphoma with t(8;14)(q24;q32); IGH@-MYC or variant MYC translocation
Mantle cell lymphoma with t(11;14)(q13;q32); CCND1-IGH@
ALK(+) DLBCL with t(v;2p23); ALK1
Viral Oncogenic Role
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in Burkitt lymphoma and plasmablastic lymphoma
MICROSCOPIC FINDINGS
Blood
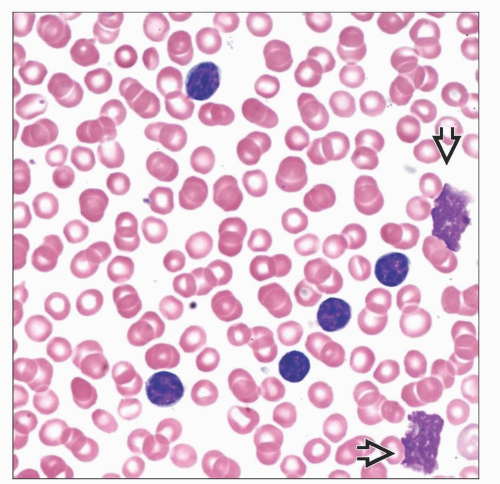
Circulating tumor cells in CLL/SLL, B-PLL, SMZL, HCL, MCL
Occasional circulating tumor cells in myeloma, LPL, FL, BL
Distinctive morphology
CLL/SLL: Small, clumped chromatin, scant cytoplasm
B-PLL: Prominent central nucleoli
HCL: Reniform nucleus, circumferential cytoplasmic projections
SMZL: Round nucleus, polar villous projections
LPL: Spectrum of lymphoid, lymphoplasmacytic, and plasma cells
Myeloma: Plasma cells
FL: Small, deeply clefted nuclei, scant cytoplasm
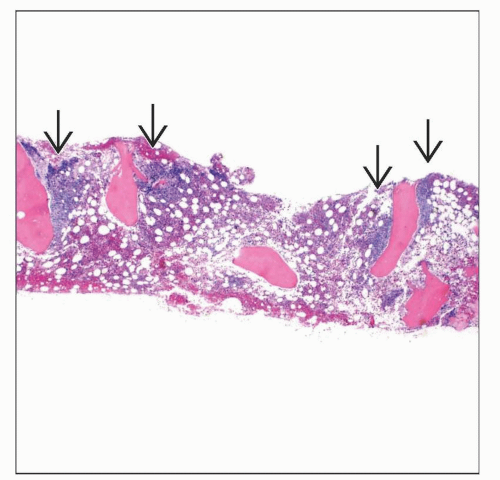
Bone Marrow
Distinctive patterns of involvement depending on B-cell leukemia, lymphoma, or PC subtype
Focal nonparatrabecular
CLL/SLL
Focal paratrabecular
FL, MCL
Diffuse/interstitial
B-PLL, HCL, LPL, DLBCL, BL
Sinusoidal
SMZL, intravascular LBCL
ANCILLARY TESTS
Immunohistochemistry
Pan B-cell antigens: CD19, CD20, CD79-α
Plasma cell-associated antigens: CD38, CD138, cytoplasmic κ, cytoplasmic λ, MUM1
Germinal center associated antigens: CD10, Bcl-6
ALK
EBER
Annexin-A1; hairy cell leukemia (HCL)
Cyclin D1; mantle cell lymphoma, HCL, PCM
Flow Cytometry
Assess surface/cytoplasmic light chain restriction
Assess aberrant/restricted antigen expression; CD5, CD10
Discriminate mature from immature; CD34, TdT
Molecular
PCR
Clonal IGH@ in mature B and PC neoplasms
Cytogenetics/FISH
For diagnosis
t(14;18)(q32;q21); BCL2-IGH@
FL
Subset of DLBCLS
Subset of double-hit lymphomas
t(8;14)(q24;q32); MYC-IGH@ or variant (Ig-MYC)
BL
Double-hit lymphomas
Subset of progressive B-cell lymphomas and myeloma
t(11;14)(q13;q32); CCND1/IGH@
MCL
For prognosis
CLL
Deletion TP53, ATM, 13q14, 13q34, IGH@ translocations, and trisomy 12 by FISH
Plasma cell myeloma
Conventional cytogenetics: Hyperdiploid favorable; hypodiploid less favorable
FISH: TP53 (17p13) deletion, t(14;16), t(4;14) less favorable
Double-hit lymphoma
Presence of t(14;18)(q21;q32) and t(8;14) (q24;q32), or t(8;14) and other BCL2 or BCL6 translocation
Highly aggressive
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Nonneoplastic B-cell or Plasma Cell Proliferations
Chronic infection
Chronic immune response
Collagen vascular diseases
Benign Lymphoid Aggregates
Immature B-cell Process
B lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma
CD34(+), TdT(+), sIg(-), CD45 weak(+) or (-)
Benign Hematogones
Characteristic dense nuclear chromatin
May mimic mature leukemias/lymphomas
Characteristic B-cell maturation pattern by flow cytometry
DIAGNOSTIC CHECKLIST
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree