Quick Question
Which structure of your eye defines its color? For the answer, review your eye anatomy.
The vascular layer of the eye is called choroid. The anterior and thickest portion of choroid is the ciliary body. The ciliary body secretes aqueous humor from structures called ciliary processes. Ciliary muscle arises in the ciliary body and attaches to the lens, altering its shape to accommodate near or distant vision. The iris is attached to the ciliary process and is positioned between the cornea and lens. The pigmented iris consists of radial and circular muscle fibers whose function is to change the size of its opening, called the pupil. The pupil regulates the amount of light entering the eye by constricting (making an opening smaller) or dilating (making an opening larger). The nervous layer of the eye, called the retina, is present only posteriorly and covers the choroid. Images focused onto the retina trigger sensory receptors characterized as rods and cones. Signals are then transmitted via the optic nerve to the occipital lobe of the brain for recognition.
The lens is positioned just behind the iris and serves to focus images onto the retina. The lens consists of protein fibers arranged in onion-like layers. The lens, which is normally transparent, is covered by a clear fibrous capsule and held in place by suspensory ligaments called zonula.
Ophthalmic prep solutions
Irrigation solutions and lubricants
Viscoelastic agents (OVD)
Miotics
Mydriatics and cycloplegics
Ophthalmic anti-infectives
Anesthetics
Antiglaucoma agents
Anti-inflammatory agents
Diagnostic agents
OVD, ophthalmic viscosurgical device.
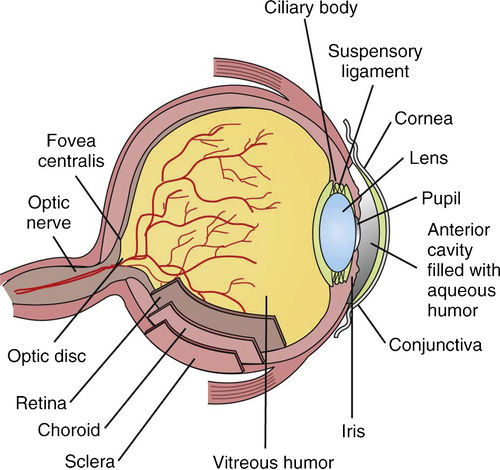
FIGURE 10-1 Anatomy of the eye. (From Young AP, Proctor DB: Kinn’s the medical assistant: an applied learning approach, ed 11, St Louis, 2011, Saunders.)
 Make it Simple
Make it SimpleThe parts of the ocular lens may be compared with a pitted fruit, such as a peach. The nucleus of the lens is like the pit of the fruit, the cortex of the lens is like the flesh of the fruit, and the lens capsule is like the skin of the fruit.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


