Oculocerebrorenal Syndrome of Lowe
Ami Bhalodia, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Oculocerebrorenal syndrome (OCRL)
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Inherited mutation caused by OCRL1 gene mutation
Affects protein trafficking and cellular metabolism
Clinical Issues
X-linked disorder; 1:200,000-1:500,000 births
Proximal tubular dysfunction, congenital cataracts, and cognitive impairment
Microscopic Pathology
Tubular and interstitial abnormalities most frequent
Dilated tubules with protein casts
Tubular atrophy and interstitial fibrosis
Medullary nephrocalcinosis
Glomerular disease is rare
Diffuse mesangial sclerosis
Ancillary Tests
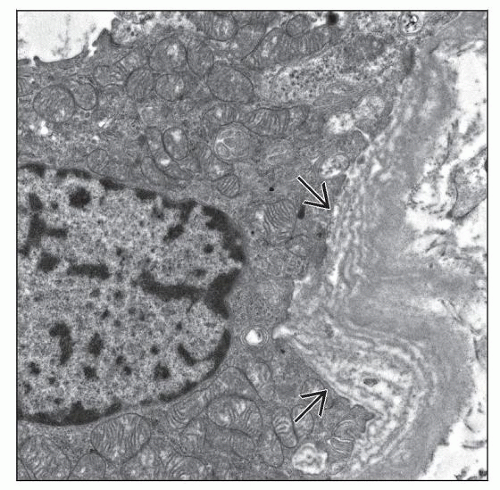
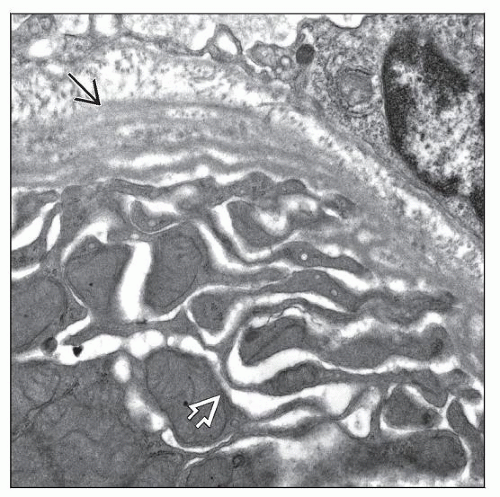
Electron microscopy
Dilated proximal tubular infolding
Proximal tubular basement membrane lamellar thickening
Tubular mitochondrial swelling and irregularity
Irregular glomerular basement membrane thickening
Top Differential Diagnoses
Dent disease
Cystinosis
Fanconi syndrome
Hypophosphatemic rickets
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Oculocerebrorenal syndrome of Lowe (OCRL)
Synonyms
Oculocerebrorenal dystrophy
Definitions
Disease triad of renal tubular dysfunction, congenital cataracts, and mental retardation due to mutations in OCRL (OMIM #309000)
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
X-linked Genetic Disease
Mutations in OCRL gene (Xq26.1)
Heterogeneous: Premature stop codons, insertion/deletion, splice site, and missense mutations
OCRL encodes OCRL1 protein
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-biphosphate 5-phosphatase
Binds to clathrin
Regulates clathrin-mediated protein trafficking
Affects vesicle-dependent proximal tubule reabsorption and trafficking of transporter proteins
Small molecular weight proteins, albumin, aminoacids, bicarbonate, calcium
Lysosomal enzymuria due to altered trafficking
Glucose transport not affected
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
1:200,000-1:500,000 births
Pan-ethnic disorder
Gender
Almost all males
Females with X-autosomal translocations reported
Presentation
Hypotonia and cataracts at birth
Glaucoma (˜ 50%)
Severe mental retardation (˜ 33%)
Seizures (˜ 50%)
Metabolic acidosis
Bicarbonate wasting, moderate
Not Fanconi syndrome, no glycosuria, mild phosphaturia
Low-grade proteinuria
Chronic renal disease by 2nd decade
Cryptorchidism
Laboratory Tests
Hypokalemia, hypocalcemia, low bicarbonate
Assessment of proximal tubular function
Low molecular weight proteinuria (e.g., retinol binding protein) (100%)
Lysosomal enzymuria (N-acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase) (100%)
Generalized aminoaciduria (˜ 90%)
Hypercalcuria (˜ 95%)
Increased alkaline phosphatase
Genetic tests for OCRL mutations
Treatment
Renal tubular acidosis
Monitor acid-base status and electrolyte levels
Potassium and calcium supplementation
˜ 50% require bicarbonate supplementation
Prognosis
Renal failure occurs in 2nd to 4th decade
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree