Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
25-60 years (average: 50 years)
Diffuse, bilateral process, predominantly distributed in lower lobes
Dyspnea
Cough
Fever
Disease has insidious onset with slowly progressive exertional dyspnea over 8-18 months
Dramatic response to corticosteroids during early stages
> 75% of patients will improve or recover completely following treatment with corticosteroids
Microscopic Pathology
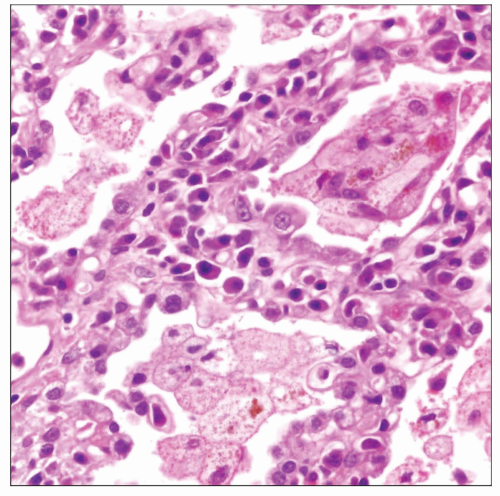
Process is characterized by interstitial fibrosis and inflammation in varying proportions
Findings are characterized by absence of temporal heterogeneity (i.e., all lesions in same stage of evolution)
Underlying lung architecture is often preserved
2 major patterns are recognized
Cellular pattern is characterized by dense lymphoid infiltration of alveolar septa with preservation of underlying lung architecture
Fibrosing pattern is characterized by uniform expansion of alveolar septa by collagen deposition, without fibroblastic foci
Diagnostic Checklist
Not a specific pathologic entity but a reaction pattern to unknown underlying stimulus
Diagnosis of exclusion (i.e., absence of features of UIP, DIP, LIP, BOOP, etc.)
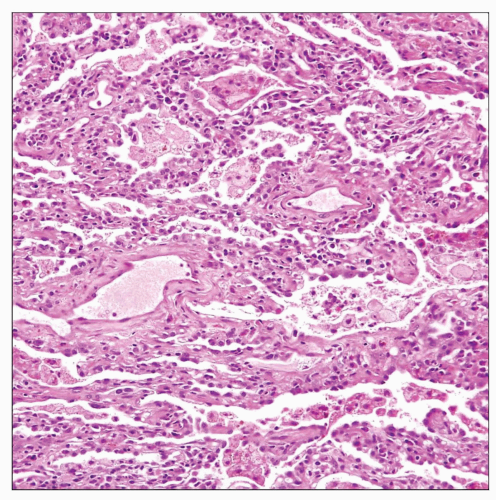 Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia pattern in the lungs shows uniform thickening of the alveolar septa with a monotonous population of inflammatory cells showing temporal uniformity. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP)
Definitions
Special pattern of fibrosing idiopathic interstitial pneumonia with much better prognosis than usual interstitial pneumonia
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Etiology
Unknown
Substantial number of cases are related to underlying collagen-vascular disease
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Age
25-60 years (average: 50 years)
Gender
Slightly more common in women
Site
Diffuse, bilateral process, predominantly distributed in lower lobes
Presentation
Dyspnea
Cough
Fever
Clubbing of fingers (up to 40% of patients)
Natural History
Disease has insidious onset with slowly progressive exertional dyspnea over 8-18 months
Dramatic response to corticosteroids during early stages
Fibrosing histologic variant of NSIP has worse prognosis than nonfibrosing (“cellular”) variant
Average 5-year survival > 80%
Treatment
Drugs
Dramatic response to corticosteroids, especially during early phases of process
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree