29 Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Prostaglandins
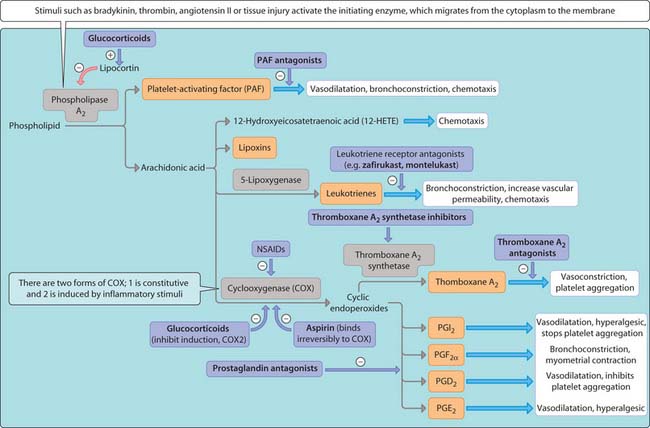
Prostaglandins belong to a family of mediators known as eicosanoids, which act by both autocrine and paracrine mechanisms. Actions are short lived as they are rapidly metabolized and not stored. Chemical signals released under physiological conditions or following tissue injury stimulate target cells, triggering a rise in intracellular Ca2+. This activates phospholipase A2, which catalyses the biosynthesis of arachidonic acid from membrane phospholipids (Fig. 3.29.1). Arachidonic acid is converted to prostaglandin (PG) H2 (an intermediary in the synthesis of prostaglandins) by cyclooxygenase (COX), of which there are two isoforms. COX1 is constitutively expressed and responsible for the production of prostanoids involved in important physiological actions (e.g. protecting the lining of the gastrointestinal tract from the corrosive action of gastric acid). The expression of COX2 is increased (i.e. is inducible) under inflammatory conditions through the action of cytokines on target cells. This leads to overproduction of prostaglandins, which are implicated in various conditions (e.g. rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, osteoarthritis).
The pharmacological activity of prostaglandins is mediated by a number of different receptor subtypes that belong to the family of G-protein-coupled receptors with seven membrane-spanning domains and this explains their considerable biological activity (Fig. 3.29.1). For example, prostaglandins like PGI2 and PGE2 have cytoprotective action in the gastrointestinal tract by stimulating bicarbonate formation, mucus secretion and blood flow to the gastric mucosa and inhibiting gastric acid secretion by parietal cells. In the kidney, prostaglandins stimulate vasodilatation in the renal medulla and glomeruli, thereby increasing blood flow and excretion of salt and water.
Pharmacological uses
There are a number of indications for the use of synthetic prostaglandin analogues. For example, dinoprostone (PGE2), carboprost tromethamine (15-methyl PGF2α) are used as abortifacients. The intracavanosal injection of alprostadil (PGE1) is used in the treatment of impotence. Misoprostol (oral acting analogue of PGE1) is used in anti-ulcer treatment to protect against erosion of the stomach in patients taking NSAIDs, and latanoprost (analogue of PGF2α) is used to promote drainage of aqueous humour for the treatment of glaucoma.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree