Neurofibromatosis Type 1
Yaxia Zhang, MD, PhD
Vania Nosé, MD, PhD
Key Facts
Terminology
Autosomal dominant tumor disorder, which results from a mutation in NF1 gene
Characterized by pigmentary or neoplastic involvement of neural crest and bony dysplasia
Clinical Issues
Café au lait patches
Neurofibromas
Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST)
Freckling in axillary or inguinal region
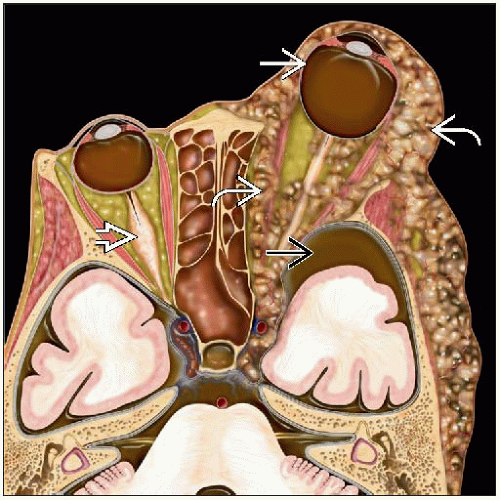
Optic nerve glioma
Lisch nodules
Duodenal carcinoid
Pheochromocytoma
Bone lesions
Neurobehavioral abnormalities
Microscopic Pathology
Plexiform neurofibroma
Tortuous proliferation of all components of peripheral nerves including axons, Schwann cells, fibroblasts, and perineurial cells
Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST)
Often high grade, poorly differentiated, and aneuploid
Optic nerve glioma (ONG)
Fibrovascular septa within optic nerve are separated by tumor cells
Top Differential Diagnoses
McCune-Albright syndrome
Neurofibromatosis type 2
Hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer
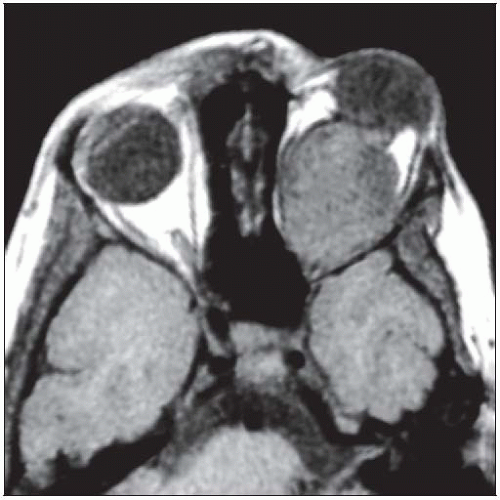 Axial T1WI MR in a young girl with NF1 reveals a massive optic nerve glioma that nearly fills the orbit. Notice the resultant proptosis and remodeling of the posterior orbit. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1)
Synonyms
von Recklinghausen disease
Peripheral neurofibromatosis
Definitions
Autosomal dominant inherited tumor disorder with high gene penetrance, which results from a mutation in NF1 gene on chromosome 17
Characterized by pigmentary or neoplastic involvement of neural crest and bony dysplasia
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Etiology
Result from a mutation in or deletion of NF1 gene encoding neurofibromin
Neurofibromin is tumor suppressor, which downregulates p21-RAS oncoprotein
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
1:3,000
Age
Diagnosis of NF1 is often made in childhood
Presentation
Skin lesions
Café au lait patches
Can be present at birth, and nearly every affected child has > 6 by age 5 or 6
Often 1st feature of NF1
Patches are usually round to ovoid, light brown in color with smooth borders, located over nerve trunks
Borders of patches are smooth, so-called “coast of California”
Neurofibromas
Cutaneous neurofibromas are soft, sessile, or pedunculated lesions that vary in number
Subcutaneous neurofibromas are often firm, round masses that are often painful
Plexiform neurofibromas, which contain numerous tortuous thickened nerves, are pathognomonic for NF1
Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST)
Most common frequent malignant neoplasms associated with NF1
Occurs in 10% of NF1
Often large, irregular, painful mass with rapid expansion
Hematogenous metastasis to lung can occur
50% of MPNSTs are associated with NF1
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree