Neurofibroma
Amitabh Srivastava, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Benign peripheral nerve sheath tumor with heterogeneous admixture of axons, Schwann cells, perineurial cells, and fibroblasts
Most are sporadic; neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) associated with multiple, large, or plexiform tumors
Clinical Issues
Localized cutaneous NF most common subtype
Diffuse cutaneous NF infiltrate dermis and subcutis
Localized intraneural NF are deep seated and involve larger nerves
Plexiform NF involves multiple nerve fascicles or branches (“bag of worms”)
Massive soft tissue NF involves pelvis, shoulder, or extremities (“localized gigantism”)
Macroscopic Features
Variable size and consistency
Lack degenerative changes seen in schwannomas
Microscopic Pathology
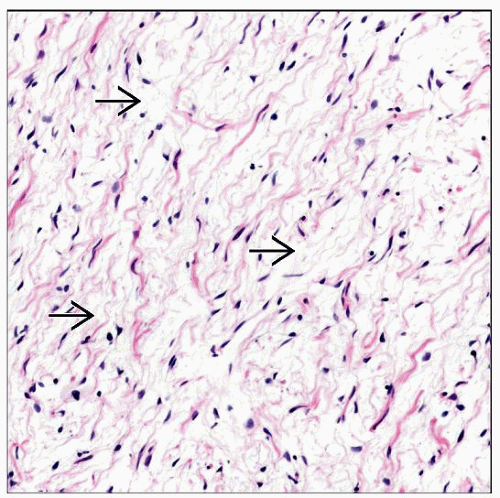
Bundles of spindle cells with angulated or wavy nuclei
Loose, myxoid, or thick collagenous matrix
Coarse collagen bundles resemble “shredded carrots”
Residual, central, neurofilament-positive axon fibers present
Atypical NF behave in benign manner
Diagnostic Checklist
Malignant transformation occurs in about 2-10% of plexiform NF
↑ cellularity, atypia, hyperchromasia, mitoses
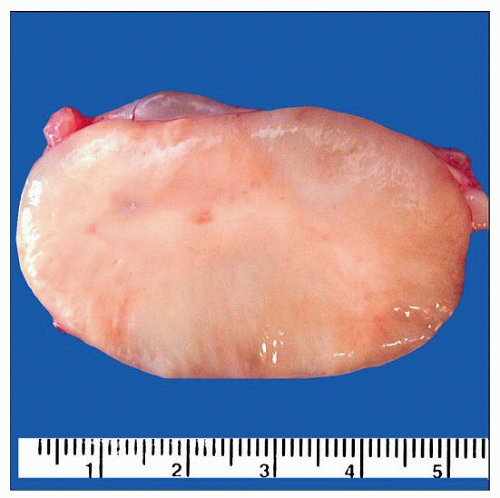 The cut surface of neurofibroma is pale, homogeneous, waxy, and often myxoid in appearance. Degenerative changes typically seen in schwannomas are seldom present in neurofibroma. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Neurofibroma (NF)
Synonyms
von Recklinghausen disease = neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1)
Definitions
Benign peripheral nerve sheath tumor composed of Schwann cells, fibroblasts, perineurial-like cells, and residual nerves in myxoid/collagen matrix
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Histogenesis
Neurofibromas are sporadic in about 90% of cases; others are syndromic in association with NF1
NF1 results from germline mutation in NF1 gene on chromosome 17q11.2
NF1 gene encodes for neurofibromin protein, which is a GTPase-activating protein
Neurofibromin also acts as a tumor suppressor by downregulating the Ras signal transduction pathway
Sporadic tumors arise from somatic mutations in NF1
Evidence supporting neoplastic nature of NF
Sporadic tumors are histologically similar to NF1-associated neurofibromas
Tumors are monoclonal on X chromosome inactivation studies
Lesional cells carry NF1 gene deletion
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Most common tumor of peripheral nerve
NF1 incidence: 1 in 2,500-4,000 births
Age
Solitary, sporadic lesions: In patients 20-30 years old
Tumors in setting of NF1 present during puberty
Plexiform NF may be congenital
Gender
Affects both sexes equally
Presentation
Most tumors are solitary and sporadic
Superficial cutaneous or localized intraneural NF present as painless, palpable mass
Deep intraneural tumors may present with pain or dysesthesia
Intraspinal (nerve root) NF may show signs of spinal cord compression
Natural History
Slow-growing tumors in most instances
Increased rates of growth may be seen in puberty and pregnancy
Malignant transformation in NF
Rare in sporadic tumors; usually occurs in setting of NF1
Very rare in cutaneous NF (0.001%)
More common in plexiform NF (2-10%)
Clinical suspicion for malignant transformation
Rapid enlargement of preexisting NF
Pain or change in neurological symptoms
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Complete resection is curative
Decompression of spinal cord in symptomatic tumors
Prognosis
Recurrence rare, even after partial removal
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree