Nephrogenic Rests
Satish K. Tickoo, MD
Victor E. Reuter, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Abnormally persistent nephrogenic cells, capable of developing into nephroblastomas
Clinical Issues
Encountered in up to 40% of patients with Wilms tumor and > 95% in patients with bilateral tumors
Both PLNR and ILNR are observed in patients in Western countries, but PLNR are rarely, if ever, seen in Asian countries
Microscopic Pathology
PLNR usually multifocal, located at periphery of renal lobes and sharply demarcated from surrounding renal parenchyma
ILNR usually unifocal, localized within renal lobes, and poorly circumscribed with interdigitations into surrounding nephrons
Dormant NR, small rests without evidence of proliferation
Sclerosing and obsolete rests consist predominantly of tubules in fibrotic background
Hyperplastic NR, showing signs of proliferation with abundant blastemal elements and increased size
Neoplastic NR, arising within dormant, sclerosing, or hyperplastic rests
Presence of pseudocapsule important in distinguishing hyperplastic or neoplastic (adenomatous) rest from nephroblastoma
Top Differential Diagnoses
Papillary adenoma
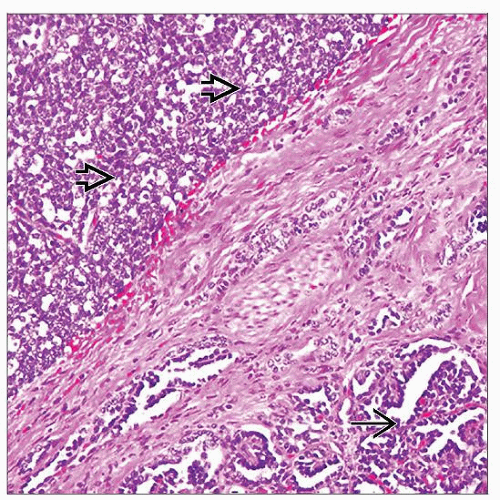
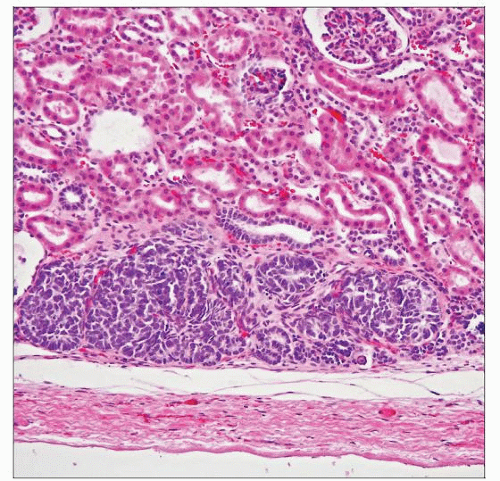 Perilobar nephrogenic rests are located at the periphery of the renal lobes, well delineated from adjacent nephrons, and composed of blastema and tubules without any significant stromal components. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Nephrogenic rest (NR), perilobar nephrogenic rest (PLNR), intralobar nephrogenic rest (ILNR)
Definitions
Abnormally persistent nephrogenic cells associated with and capable of developing into nephroblastomas
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Molecular Alterations
Like those in Wilms tumor (WT), alterations in WT1 (11p13), WT2 (11p15), and WT3 (16q) genes are present in accompanying NRs
Mutations in WT1 are present in ILNR
Insulin growth factor 2 loss of paternal imprinting (LOI) (in putative WT2 gene region) in PLNR of all types (sclerosing, hyperplastic, etc.)
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Encountered in up to 40% of patients with WT; incidence > 95% in patients with bilateral tumors
Observed in 1% of infant autopsies; isolated intralobar NRs less common (1 in 1,000 autopsies)
Age
Median at presentation: WT and ILNR = 18.5 months; WT and PLNR = 35.5 months
Gender
WT and NR show equal sex distribution or slight female preponderance in the West, but significant male preponderance in Asia
Ethnicity
PLNR somewhat more common than ILNR in West, but PLNR extremely uncommon in Asia
Treatment
Hyperplastic rests difficult to distinguish from WT on biopsy; these and later forms treated similar to stage 1 WT (National Wilms Tumor Study Group [NWTS])
Treating hyperplastic rests prevents compression and damage to native kidney
Also, treating these diminishes targets for neoplastic transformation
Prognosis
NRs in WT-bearing kidneys are associated with higher incidence of synchronous or metachronous WT in other kidney
Higher incidence of concurrent bilateral Wilms tumor in patients with NRs, particularly PLNR
Risk of metachronous WT 15x higher in children < 1 year of age with WT and NR (particularly PLNR) than those without NR
Identifying NR on nephrectomy for WT leads to increased frequency of ultrasonographic follow-up for child
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree