Myxofibrosarcoma
Thomas Mentzel, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Myxofibrosarcoma represents a spectrum of malignant fibroblastic neoplasms with variably myxoid stroma and characteristic elongated curvilinear vessels
Clinical Issues
One of the most common sarcomas in elderly patients
Majority arises in limb, including limb girdles (lower > upper extremities)
2/3 of cases arise in dermal/subcutaneous tissues
Local, often repeated recurrences in up to 50-60% of cases unrelated to histologic grade
Intermediate- and high-grade malignant neoplasms may develop metastases in 30-35% of cases
Macroscopic Features
Superficially located neoplasms consist of multiple, variably gelatinous or firmer nodules
Deep-seated neoplasms often present as single mass with myxoid cut surfaces
Microscopic Pathology
Broad spectrum of cellularity, cytologic atypia, and proliferative activity reflected by 3 grades of malignancy
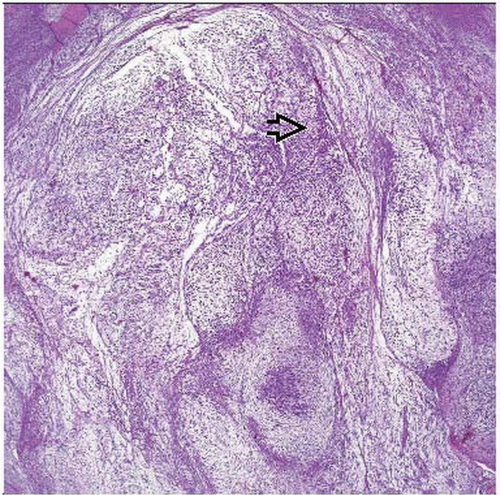
Multinodular growth, spindled and stellate atypical fibroblastic cells
Myxoid stroma with elongated, curvilinear, thin-walled vessels
Often pseudolipoblasts are present
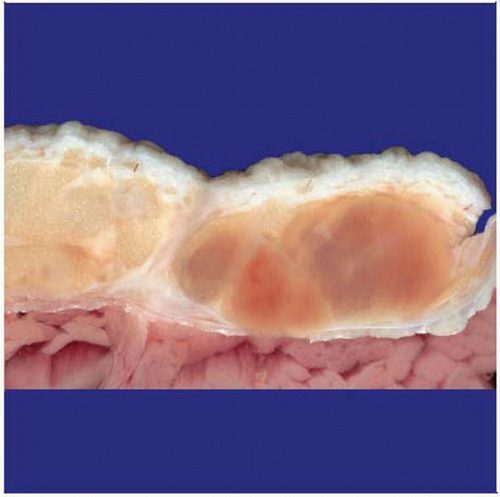 Grossly, cases of myxofibrosarcoma often show a multinodular growth with myxoid cut surfaces, as shown here. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Myxofibrosarcoma (MFS)
Synonyms
Myxoid malignant fibrous histiocytoma
Definitions
Myxofibrosarcoma represents a spectrum of malignant fibroblastic neoplasms with variably myxoid stroma and characteristic elongated curvilinear vessels
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
One of the most common sarcomas in elderly patients
Age
Affects mainly patients in 6th-8th decade
Exceptionally rare in patients < 20 years old
Gender
Slight male predominance
Site
Majority arise in limbs, including limb girdles (lower > upper extremities)
More rarely on trunk, head and neck region
Very rarely on hands and feet
Extremely rare in retroperitoneum and in abdominal cavity
2/3 of cases arise in dermal/subcutaneous tissues
Presentation
Painless mass
Slow growing
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Complete wide excision
Prognosis
Local, often repeated recurrences in up to 50-60% of cases unrelated to histologic grade
Low-grade malignant neoplasms usually do not metastasize
May show tumor progression in subsequent recurrences and may acquire metastatic potential
Intermediate- and high-grade malignant neoplasms may develop metastases in 30-35% of cases
Overall 5-year survival is 60-70%
Depth of lesions and grade of malignancy do not influence recurrence rate
Percentage of metastases and tumor-associated mortality are higher in deep-seated neoplasms & high-grade malignant neoplasms
Local recurrences within < 12 months increase tumor associated mortality
Proliferative activity, percentage of aneuploid cells, and tumor vascularity are associated with histologic tumor grade
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Superficially located neoplasms consist of multiple, variably gelatinous or firmer nodules
Deep-seated neoplasms often present as single mass with myxoid cut surfaces
Areas of tumor necrosis may be seen in high-grade neoplasms
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Broad spectrum of cellularity, cytologic atypia, and proliferative activity reflected by 3 grades of malignancy
Low-grade malignant myxofibrosarcoma
Hypocellular neoplasms
Few noncohesive tumor cells
Ill-defined eosinophilic cytoplasm
Enlarged hyperchromatic nuclei
Intermediate-grade malignant myxofibrosarcoma
More cellular and pleomorphic than low-grade neoplasms
No solid areas
No tumor necrosis
High-grade malignant myxofibrosarcoma
Large parts are composed of solid sheets and cellular fascicles
Spindled and pleomorphic tumor cells
Bizarre, multinucleated tumor giant cells
Numerous, often atypical mitoses
Areas of tumor necrosis may be present
At least focally, areas of lower grade neoplasm with prominent myxoid stroma and numerous curvilinear vessels
Multinodular growth with incomplete fibrous septa
Myxoid stroma
Prominent elongated, curvilinear, thin-walled blood vessels
Foci of inflammatory cells may be present
Cytologic Features
Spindled and stellate atypical fibroblastic cells
Often pseudolipoblasts are present
Pseudolipoblasts are vacuolated neoplastic fibroblastic cells
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree