Myeloproliferative Neoplasm, Unclassifiable
Kaaren K. Reichard, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Definition
Clonal hematopoietic neoplasm
Meets criteria for an MPN
Features are not sufficient to render more specific MPN diagnosis
Microscopic Pathology
Early phase of disease
Thrombocytosis
Mild neutrophilic leukocytosis
Blasts < 10%
BM hypercellular
Abnormal megakaryocytic proliferation
Minimal fibrosis
Late phase of disease
Leukoerythroblastosis
Increased blast %
Osteosclerosis
Marked fibrosis
Ancillary Tests
Immunophenotyping
CD34
Conventional cytogenetics
Exclude BCR-ABL1 fusion and rearrangements of PDFGRA, PDGFRB, and FGFR1
Molecular genetics
JAK2 V617F may be present; not specific
Top Differential Diagnoses
Specific MPN subtype
Reactive conditions
Underlying malignancy
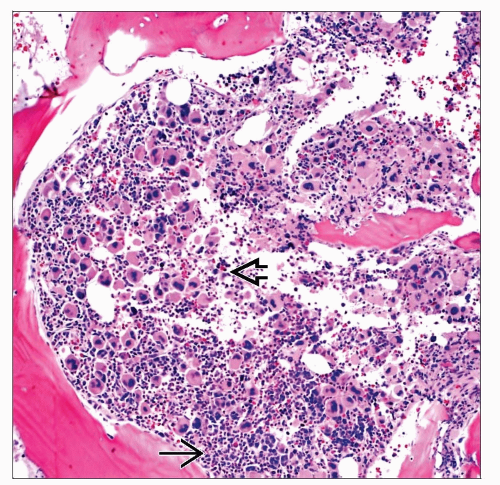
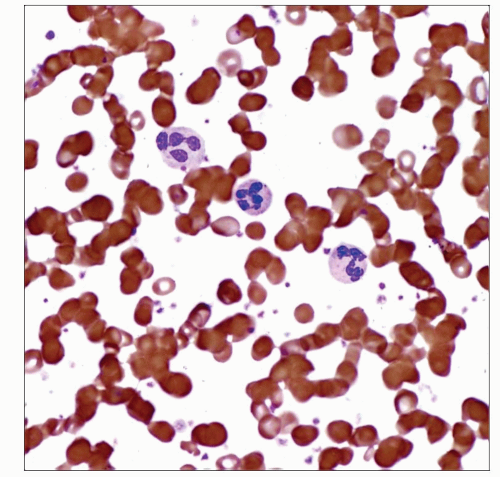 PB smear shows moderate thrombocytosis and neutrophilic leukocytosis in a case of MPN-U. Criteria for a specific MPN subtype were not met. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Myeloproliferative neoplasm, unclassifiable (MPN-U)
Synonyms
Myeloproliferative disorder, unclassifiable
Myeloproliferative neoplasm, not otherwise specified
Definitions
Clonal hematopoietic neoplasm
Diagnostic criteria for MPN are met
Features are not sufficient to render more specific MPN diagnosis
Early disease presentation
End-stage disease precluding recognition of more specific underlying MPN
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Unknown
No definite etiology has been identified
Molecular Mutations
May be present (e.g., JAK2 V617F)
Likely pathogenetic to some extent
No specific mutations known so far
Confirms clonal disorder
CLINICAL ISSUES
Site
Peripheral blood (PB)
Bone marrow (BM)
Spleen
Liver
Presentation
Similar to other MPNs
Early disease
Variable cytoses
Unexplained deep-seated thrombotic events
No significant % blasts
Late-stage disease
Leukoerythroblastosis
Cytopenias
Marked hepatosplenomegaly
Increased blasts
Ultimate BM failure
Laboratory Tests
Complete blood cell count (CBC) with differential
PB and BM examination
Conventional cytogenetics
Exclude BCR-ABL1 fusion and rearrangements of PDGFRA, PDGFRB, and FGFR1
Molecular studies
JAK2 V617F mutation
Prognosis
Early disease
Specific MPN subtype may emerge
Outcome related to specific subtype
Late disease
Generally poor outcome
Bone marrow failure
Extensive BM fibrosis or increased blasts
Refractory splenomegaly
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Typical Presentation of MPN-U
Peripheral Blood Microscopic Features
Early phase of disease
Thrombocytosis
Mild neutrophilic leukocytosis
Blasts < 10%
Normal hemoglobin or mild anemia
Late phase of disease
Leukoerythroblastosis
Left shift in granulocytes
Variable % blasts
Teardrop-shaped red blood cells
Nucleated red blood cells
Bone Marrow Microscopic Features
Early phase of disease
BM often aspirable
Hypercellular
Abnormal megakaryocytic proliferation
No significant/mild reticulin fibrosis
Myelodysplastic features unusual
Consider myelodysplastic syndrome or myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasm
Occasional granulocytic &/or erythroid prominence
No bony changes
Late-stage disease
Marked reticulin fibrosis
Collagen fibrosis
Osteosclerosis
10-19% PB &/or BM blasts
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree