Myeloma Cast Nephropathy
Anthony Chang, MD
Lynn D. Cornell, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Synonyms
Light chain cast nephropathy
Myeloma kidney
Accumulation of monoclonal light chains may form casts (both cytotoxic and obstructive) in distal nephron segments
Clinical Issues
Acute renal failure
30-50% incidence among patients with multiple myeloma
5-year survival rate of 20-25%
Microscopic Pathology
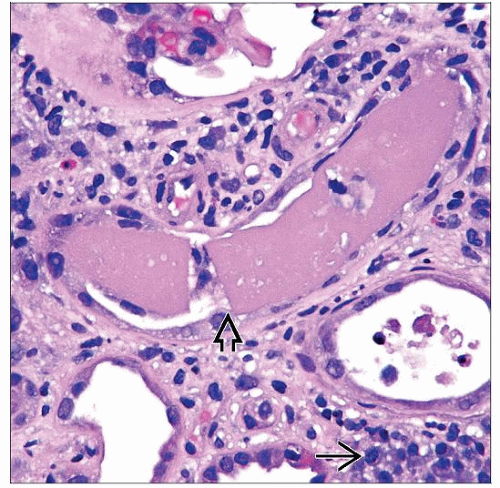
Tubular casts
Usually involve distal nephron segments (distal tubules and collecting ducts)
Sharp-edged or fractured appearance
Giant cell reaction to intratubular casts
Prominent intratubular aggregates of neutrophils can be present
Ancillary Tests
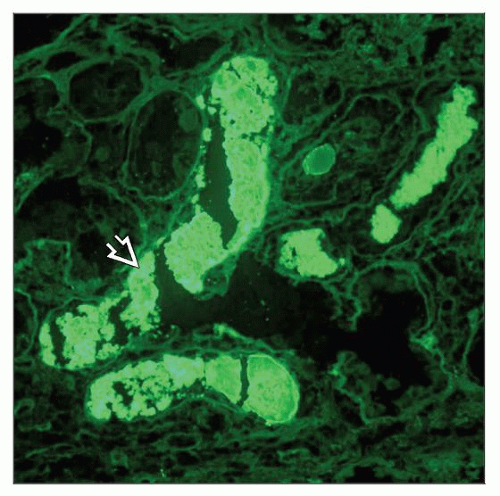
Immunofluorescence or immunohistochemistry
Kappa is more common than lambda with ratio ranging from 2:1 to 4:1
Top Differential Diagnoses
Rhabdomyolysis-associated acute tubular injury
mTOR inhibitor toxicity
Monoclonal immunoglobulin deposition disease
Acute tubular injury
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Myeloma cast nephropathy (MCN)
Synonyms
Light chain cast nephropathy
Bence Jones cast nephropathy
Myeloma kidney
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Plasma Cell Dyscrasia
Monoclonal light chain overproduction
Light chains (Bence Jones proteins) freely filtered by glomeruli
Not all monoclonal light chains are nephrotoxic
Accumulation of Tamm-Horsfall protein and monoclonal light chains in distal nephron segments may lead to both obstruction and direct cytotoxicity
Precipitating factors for cast formation include
Dehydration
Diuretics
Hypercalcemia
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Contrast media
Infections
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
30-50% among patients with multiple myeloma
Age
Typically > 40 years
Gender
Male > female
Presentation
Acute renal failure & proteinuria
Laboratory Tests
Serum &/or urine protein electrophoresis
Immunoelectrophoresis
Immunofixation electrophoresis
Treatment
Drugs
Treatment for underlying plasma cell dyscrasia, if present
Colchicine, thalidomide, bortezomib
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Plasmapheresis
Prognosis
5-year survival rate of 20-25%
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Tubular casts
Usually involve distal nephron segments (distal tubules and collecting ducts)
PAS negative (vs. Tamm-Horsfall protein [THP])
Trichrome stains red (vs. blue THP)
Sharp-edged or fractured appearance
Lined by flattened to reactive tubular epithelial cells
Giant cell reaction to intratubular casts may be present
Prominent intratubular aggregates of neutrophils can be present
Rare crystal appearance may be present
Interstitial inflammation
Interstitial neoplastic plasma cell infiltrates may be present
Monoclonal staining by in situ hybridization or immunohistochemistry
ANCILLARY TESTS
Immunofluorescence
Kappa is more common than lambda with ratio ranging from 2:1 to 4:1
Can be performed on paraffin tissue sections with good results
Electron Microscopy
Transmission
Monoclonal light chain tubular casts demonstrate a spectrum of substructural organization
Nonspecific appearance to crystalline, granular, or even fibrillar substructure
Immunogold labeling may be more sensitive than immunofluorescence or immunohistochemistry to demonstrate monoclonality in some cases
Immunohistochemistry
κ and λ can be tested on paraffin tissue sections if tubular casts are not present in specimen submitted for immunofluorescence microscopy
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Rhabdomyolysis-associated Acute Tubular Injury
Tubular casts are pigmented with granular consistency
Absence of monoclonal immunolocalization
mTOR Inhibitor Toxicity
Reported in kidney transplant patients with delayed graft function after using an immunosuppressive regimen containing rapamycin
Tubular casts with fractured appearance
Multinucleated giant cell reaction can be present
Casts may consist of myoglobin
Monoclonal Immunoglobulin Deposition Disease
Often occurs concurrently with MCN
Amyloidosis
Concurrent amyloidosis and MCN rarely occur
Acute Tubular Injury
Proteinaceous casts are PAS positive
Absence of monoclonal staining in tubular casts
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree